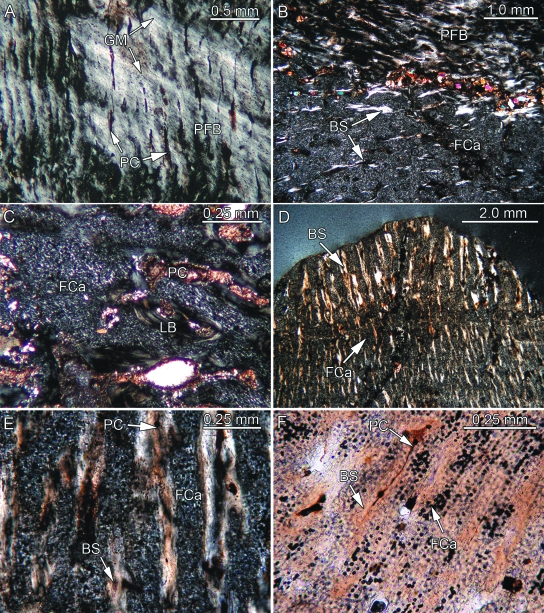
Fig. 3.
Bone histology of placodont armor plates that range from consisting partly to consisting completely of PFCB. Besides (F) all remaining images were taken in polarized light. (A) Close-up of parallel-fibered bone (PFB) and radial primary canals (PC) of external cortex of Psephosaurus sp. (SMNS 91009). (B) Close-up of transition between PFB and PFCB matrix, consisting largely of cartilage cell lacunae (FCa) and bone spiculae (BS), of the external cortex of former specimen. (C) Close-up of externally situated cartilaginous bone of cf. Placochelys sp. (SMNS 91010). Note that only a few BS are present. (D) Transition between coarse apical and fine interior PFCB of P. suevicus (SMNS 91007). Note differences in size and orientation of BS, as well as amount of interstitial FCa. (E) Close-up of the coarse PFCB of former specimen. (F) Close-up of the fine interior PFCB of former specimen. BS and PC alternate with regular layers of FCa.