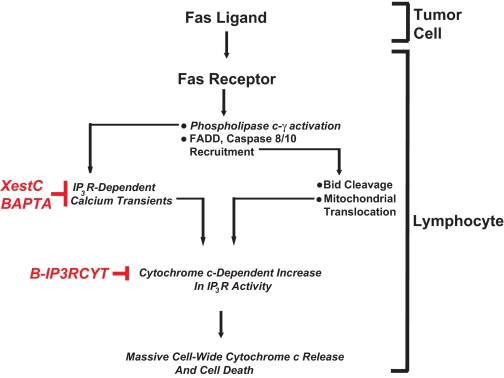
FIGURE 2.
Calcium and tumor-induced lymphocyte apoptosis. Fas ligand expressed on tumor cells activates Fas receptor on infiltrating lymphocytes. This causes activation of IP3R by coupling of Fas receptor to phospholipase C-γ1 and subsequent production of IP3 (12). The canonical components of the death-induced signaling complex are also recruited to Fas receptors such as Fas-associated death domain (FADD) and caspase 8/10. Caspase 8/10 activation induces Bid activation and translocation to mitochondria, sensitizing them to calcium-induced cytochrome c release. Cytochrome c subsequently binds to IP3R, causing further calcium release and mitochondrial calcium overload. Blocking IP3-dependent elevations in cytosolic calcium with Xestospongin C or BAPTA inhibits lymphocyte apoptosis. Specifically blocking cytochrome c binding to IP3R also inhibits lymphocyte apoptosis without modifying agonist-induced calcium release, suggesting a viable target for therapeutic intervention.