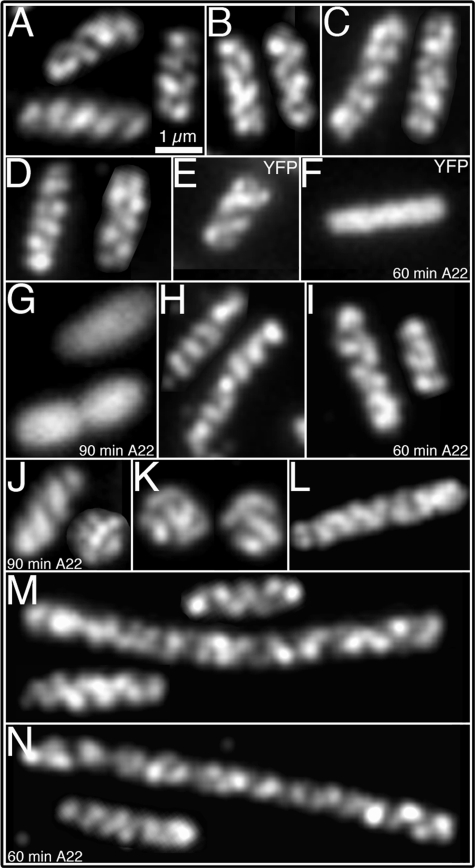
FIGURE 2.
Determinants of the cytoskeletal-like organization of RhlB. Localization of RhlB by immunofluorescence microscopy using purified anti-RhlB antibody (A–D, H–K, M, and N); localization of MreB by fluorescence from Yfp-labeled MreB (E–G); and immunofluorescence localization of HA-tagged RNaseE-(1–659) using anti-HA antibody (L). A, strain AT31 (rne1–417 pnp::HA). B, strain AT45 (rne1–417::HA Δpnp). C, strain AT46 (rne::HA Δeno). D, strain AT53 (rne::HA Δpnp,Δeno). E, MC1000/Plac-yfp::mreB cells grown in the absence of A22. F and G, MC1000/Plac-yfp::mreB A22-treated cells for 60 min (F) or 90 min (G). H, strain AT27 (rne1–659::HA) grown in the absence of A22. I and J, strain AT27 (rne1–659::HA), grown in the presence of A22 for 60 min (I) or 90 min (J). K, strain YLS3 (ΔmreB). L, strain AT61 (rne1–659::HA ΔminCDE) showing the coiled structure of RNaseE-(1–659). M, RhlB localization in strain AT61 (rne1–659::HA ΔminCDE) grown in the absence of A22. N, RhlB localization in strain AT61 (rne1–659::HA ΔminCDE) treated for 60 min with A22. Because of the Min- phenotype the cells grow as a mixture of short filaments of varying cell length (35) (M, N). As previously reported, ΔmreB and cells treated with A22 for 90 min grow as spheroids of different sizes (G, J, K) (18, 26). The described localization pattern was present in 95–97% of cells (see “Experimental Procedures”). Scale bar, 1 μm.