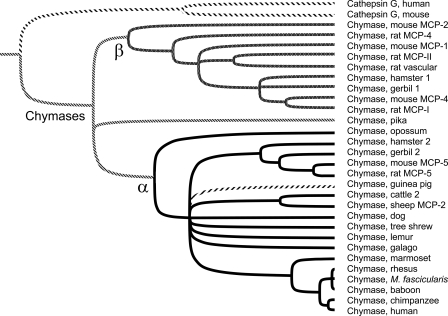
FIGURE 2.
Tree of α/β chymases. Phylogenetic relationships between guinea pig chymase and other chymases are probed with this rooted dendrogram generated by UPGMA analysis of aligned mature chymase amino acid sequences using 1000 iterations of bootstrap resampling. The threshold for node assignment was 70%. Tines of peptidases belonging to α and β clades are black and gray, respectively, except for guinea pig chymase, which is forward-hatched. Examples of cathepsin G, the closest relative of chymases, are included for comparison. Accession numbers of sequences used in tree construction are as follows: human and mouse cathepsin G (NP_001902 and CAA55290), mouse MCP-1, -2, -4, and -5 (AAB23194, NP_032597, NP_034909, and NP_034910), rat MCP-I and -II (AAB48268 and P00700), rat MCP-4 and -5 (U67907 and NP_037224), rat vascular chymase (AAC16657), hamster chymase 1 and 2 (BAA19932 and BAA28615), gerbil chymase 1 and 2 (P50340 and P50341), opossum chymase (XP_001369716), guinea pig chymase (this work; AM851020), cattle chymase 2 (XP_593156), sheep MCP-2 (P79204), dog chymase (NP_001013442), baboon chymase (AAA91159), rhesus chymase (BAA22070), M. fascicularis chymase (crab-eating macaque; BAA22070), chimpanzee chymase (XP_001170224), and human chymase (M64269). We deduced the sequence of additional chymases from unannotated whole genome shotgun sequence as follows: American pika (Ochotona princeps, AAYZ01164217), tree shrew (AAPY01734039), mouse lemur (ABDC01231172), galago (AAQR01659070), and marmoset (contig 1790.4 from the Washington University Genome Sequencing Center, available on the World Wide Web).