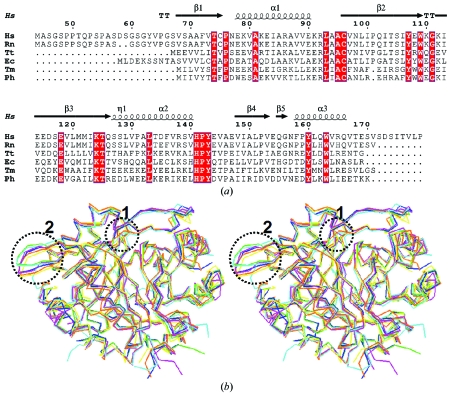
Figure 4.
(a) Sequence alignment of HsCutA1 with other selected CutA1 proteins for which three-dimensional structures are available. The secondary-structural elements shown above the sequences and the numbering of the residues refers to HsCutA1. Completely conserved residues are highlighted by white characters on a red background. Helices (α-helices) are represented by squiggles, β-strands are shown as arrows and β-turns are marked TT. This sequence alignment was created using the following sequences from the PDB: RnCutA1 (CutA1 from Rattus norvegicus; PDB code 1osc), TtCutA1 (CutA1 from Thermus thermophilus; 1nza), EcCutA1 (CutA1 from E. coli; 1naq), TmCutA1 (CutA1 from Thermotoga maritima; 1kr4; Savchenko et al., 2003 ▶), PhCutA1 (CutA1 from P. horikoshi; 1v9b). (b) Superposition of the trimers of selected CutA1 structures: HsCutA1 (green), RnCutA1 (blue), TtCutA1 (yellow), EcCutA1 (magenta), TmCutA1 (cyan) and PhCutA1 (orange). Circled area 1, the β2-strand kink observed in HsCutA1, RnCutA1, TtCutA1 and EcCutA1 but not in TmCutA1 and PhCutA1. Circled area 2, the β-hairpin turn; the largest differences in the superposition of the CutA1 trimers are found in the flexible β-hairpin turns.