FIG. 1.
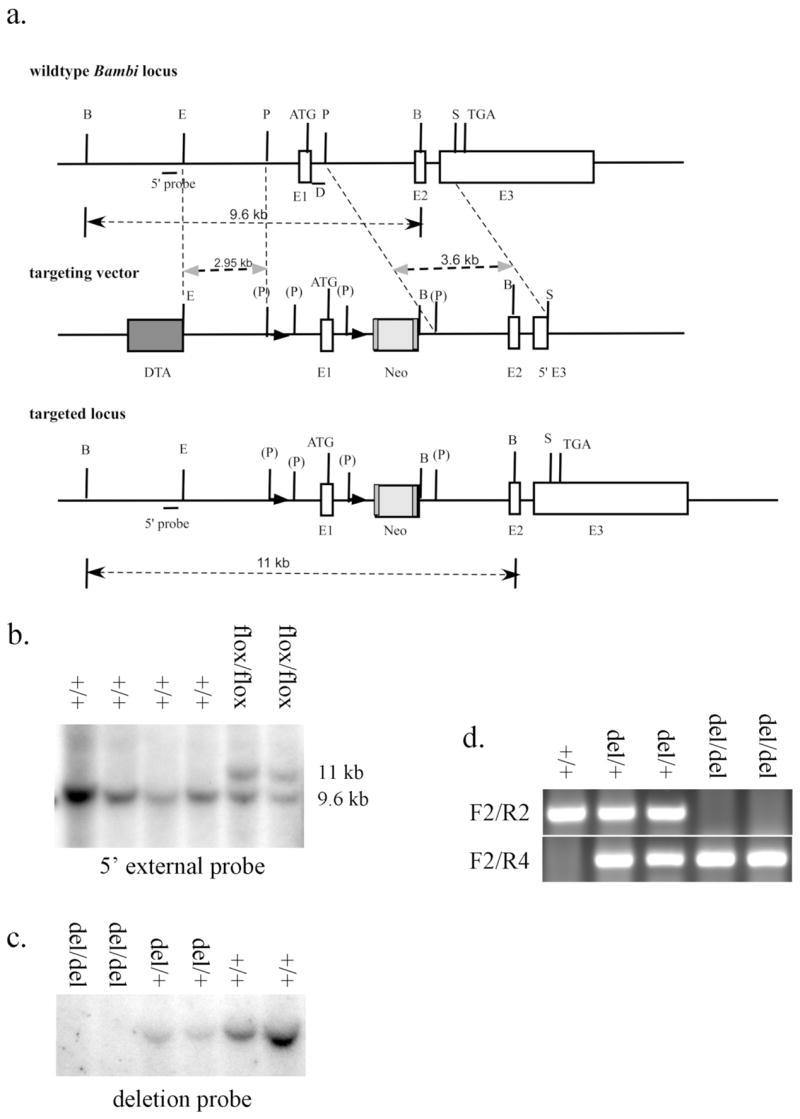
Generation of Bambiflox and Bambidel mice. (a) Schematic representation of the Bambi genomic locus, the gene targeting construct and the targeted (Bambiflox) allele. LoxP sequences are indicated by black triangles. D marks the deletion probe; DTA, diphtheria toxin A expression cassette; E1, exon 1; E2, exon 2; E3, exon 3; Neo, Frt-flanked PGK-Neo cassette. The restriction enzyme recognition sites are: B, Bgl I; E, EcoRI; P, PmlI; S, SacI. (P) marks PmlI site destroyed during subcloning. (b) Southern hybridization analysis of BglI-digested genomic DNA from representative G418-resistant ES clones using the 5′ external probe. The upper band (11 Kb) represents the targeted allele and the lower band (9.6 Kb) represents the wildtype allele. (c) Southern hybridization analysis of EcoRI-digested tail genomic DNA from Bambi+/+, Bambidel/+, and Bambidel/del mice using the deletion probe. A 7.7 Kb band was only detected in the wildtype and heterozyougs mouse DNA samples, but not in DNA from the homozygous Bambidel/del mice. (d) PCR analysis of tail DNA of Bambi+/+, Bambidel/+, and Bambidel/del mice using primers F2, R2 and R4. The upper fragment (215 bp) represents the wildtype allele, and the lower band (316 bp) represents the Bambidel allele.
