Fig. 6.
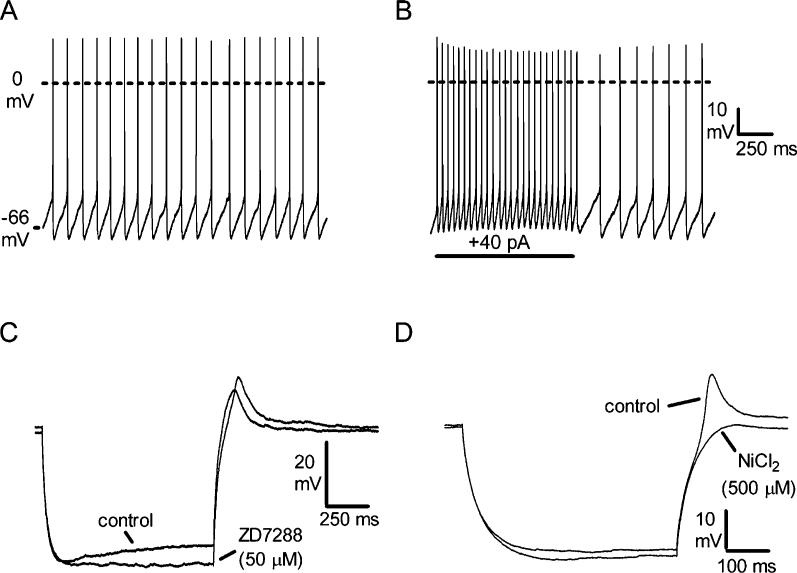
Intrinsic membrane properties of subcoeruleus (SubC) and pontine nucleus oralis (PnO) green fluorescent protein (GFP)-positive neurons (n = 61). (A) Spontaneous action potential firing (scale same as in B). (B) Increased tonic firing in response to depolarizing current step. (C) Response to hyperpolarizing current injection (−130 pA) in the presence of tetrodotoxin (TTX, 0.5 μM), illustrating a medium-sized depolarizing sag during the step that is blocked by the H-current blocker ZD7288 (n = 7/7). Note that the rebound depolarization at the offset of the step is slightly increased in size by the block of Ih. (D) Response to a smaller hyperpolarizing current step (−100 pA) in a different neuron, illustrating a rebound depolarization that is blocked by the calcium channel antagonist NiCl2 (n = 9/9).