Figure 3.
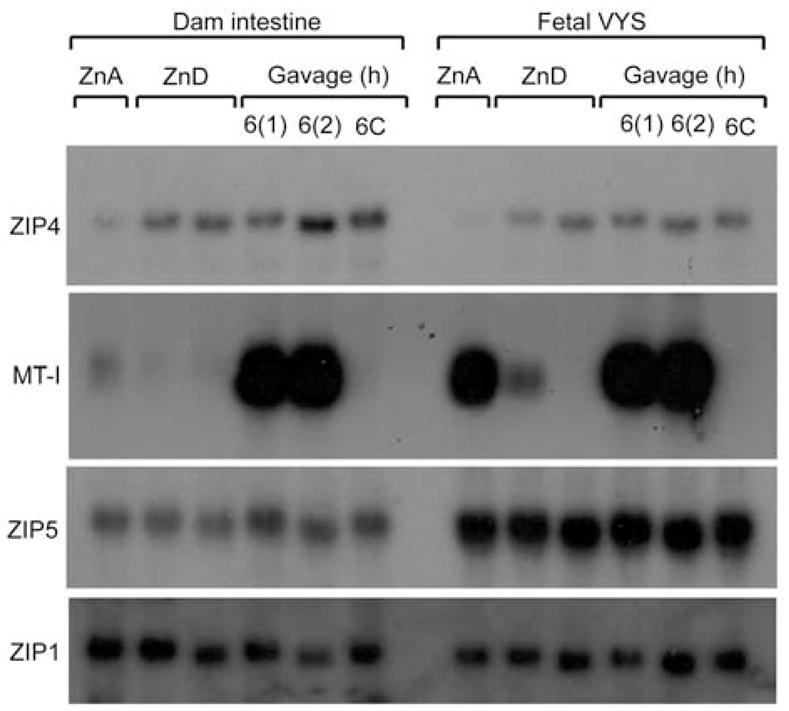
Effects of zinc repletion on Zip4 and Zip5 mRNA abundance in the proximal small intestine (duodenum) and visceral yolk sac (VYS).
Northern blot detection of Zip4, MT-I, Zip5 and Zip1 mRNAs in the maternal (dam) proximal small intestine (duodenum) and the fetal VYS is shown. Pregnant mice were fed a zinc-adequate (ZnA) or zinc-deficient (ZnD) diet for 6 days beginning on d8 of pregnancy (ending on d14). The zinc-deficient mice were then given an oral gavage of zinc or saline (6C), and tissues were harvested at the indicated times thereafter. Two independent groups of mice, labeled 6(1) and 6(2) were analyzed for the 6 h zinc-gavage time point. Specific transcripts were detected using total RNA, as described in the legend to Figure 1. Zip1 mRNA served as a good loading control, as it has equivalent expression amongst many tissues and is not zinc regulated.
