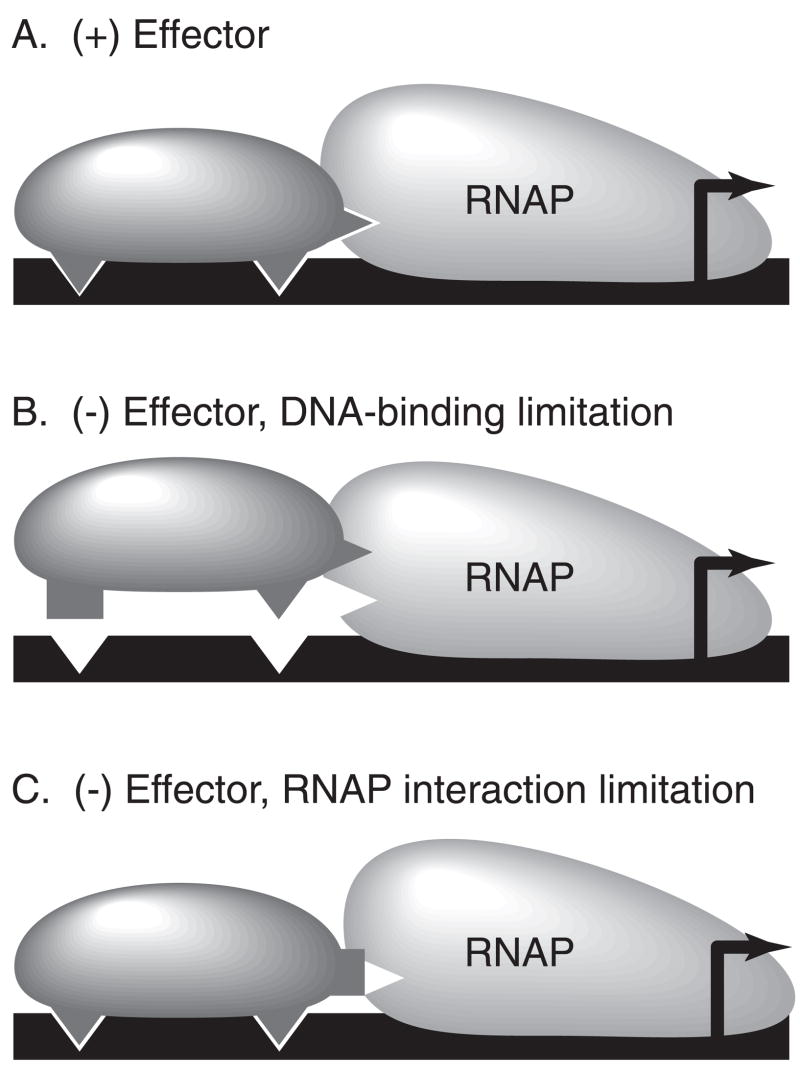
Figure 6.
Model of the effector responses of RhaS and RhaR. (A) In the presence of effector, both RhaS and RhaR can efficiently bind to DNA and contact RNAP to activate transcription. (B) In the absence of an effector, RhaS is limited in its ability to bind to DNA. (C) In the absence of effector, RhaR is limited in its ability to effectively contact RNAP. Black line, DNA; dark gray, the DNA binding domain of the promoter-proximal monomer of either RhaS or RhaR; light gray, RNAP. Triangular protrusions or indentations represent sites of contact between the DNA-binding domain of RhaS or RhaR and DNA or RNAP, whereas rectangular protrusions represent sites that are not in the correct conformation to make contact.