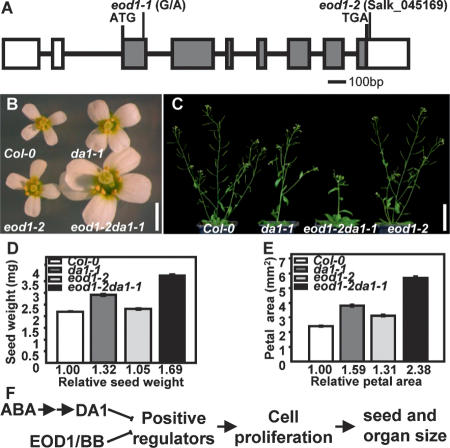
Figure 5.
Mutations in EOD1/BB synergistically enhance the phenotypes of da1-1. (A) EOD1/BB gene structure, showing the mutated sites of the two eod1 alleles. The start codon (ATG) and the stop codon (TGA) are indicated. Closed boxes indicate the coding sequence, and lines between boxes indicate introns. The mutated site in eod1-1 and T-DNA insertion site in eod1-2 also are shown. (B) Flowers of Col-0, da1-1, eod1-2, and eod1-2da1-1 double mutants. (C) Soil-grown plants of Col-0, da1-1, eod1-2da1-1 double mutant, and eod1-2 are shown. (D) Average seed weights of Col-0, da1-1, eod1-2, and eod1-2da1-1 double mutants are shown as milligrams per 100 seeds. Standard deviations are shown (n = 5). Plants were grown under identical conditions. (E) Petal areas of Col-0, da1-1, eod1-2, and eod1-2da1-1 double mutant. Standard deviation values are shown (n > 50). (F) A model of DA1 and EOD1/BB controlling seed and organ size. Bars: B, 2 mm; C, 50 mm.