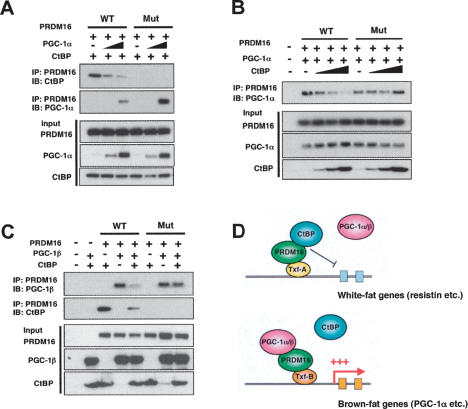
Figure 6.
PGC-1α/β and CtBP directly compete for binding to the PRDM16 complex. (A) Fixed amounts of wild-type PRDM16 (WT) or CtBP-binding-deficient mutant PRDM16 (Mut) were expressed along with fixed amounts of CtBP (CtBP-1) and variable amounts of PGC-1α in COS-7 cells. Cell lysates were incubated with Flag M2 agarose (PRDM16) and separated by SDS-PAGE. The interaction of PRDM16 with CtBP or PGC-1α was detected by Western blotting. The inputs are shown in the bottom panels. (B) Fixed amounts of wild-type PRDM16 (WT) or mutant PRDM16 (Mut) were expressed along with fixed amounts of PGC-1α and variable amounts of CtBP. Interaction of PRDM16 with CtBP was detected as described above. (C) Wild-type PRDM16 (WT) or mutant PRDM16 (Mut) were coexpressed with PGC-1β or CtBP, and the interaction of PRDM16 with PGC-1β or CtBP was examined as described above. (D) A schematic model of brown fat determination by PRDM16. PRDM16 represses white fat-selective genes such as resistin by recruiting CtBP onto their promoters. Recruitments of PGC-1α and PGC-1β to PRDM16 trigger the dismissal of CtBP from the PRDM16 complex, leading to the robust activation of brown fat-selective genes.