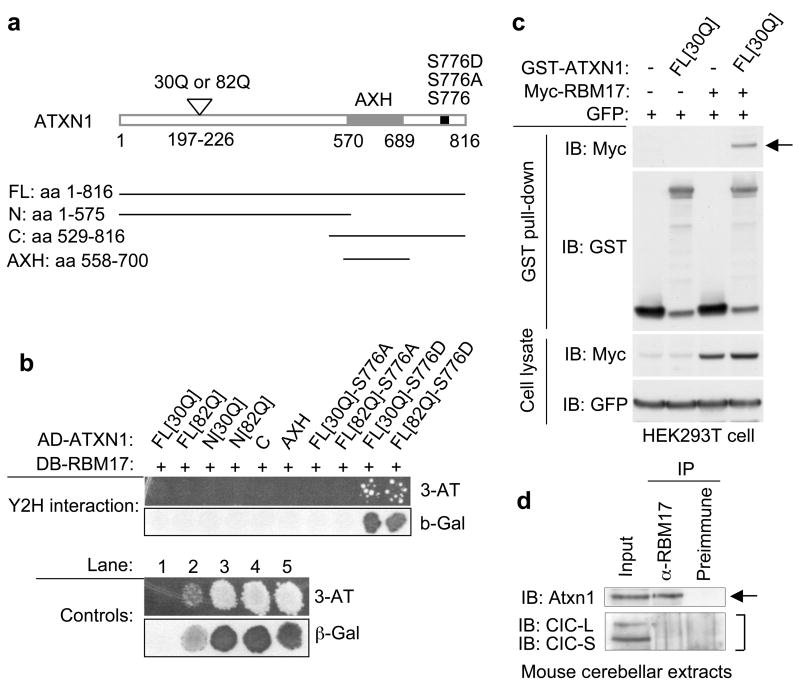
Figure 1. ATXN1-S776D but not ATXN1-S776A interacts with RBM17.
(a) Schematic representation of the ATXN1 constructs.
(b) RBM17 specifically interacted with ATXN1-S776D in the Y2H screen. AD (activation domain) and DB (DNA binding domain) of Gal4 were fused to human ATXN1 or RBM17, respectively. Y2H controls are: lane 1, negative control; lane 2, weak positive control; and lanes 3–5, strong positive controls.
(c) ATXN1 interacted with RBM17 in HEK293T cells by co-AP assays. Top panel shows expression of myc-RBM17 after affinity purification on Glutathione-Sepharose 4B beads, demonstrating the ATXN1/RBM17 interaction (arrow). GST-empty vector was used as a control (−). IB, Immunoblot.
(d) Co-IP of Atxn1 with RBM17 from wild-type mouse cerebellar extracts. The anti-RBM17 antibody co-immunoprecipitated Atxn1 (arrow), but not the long and short isoforms of Capicua, CIC-L and CIC-S, respectively (bracket).