Fig. 4.
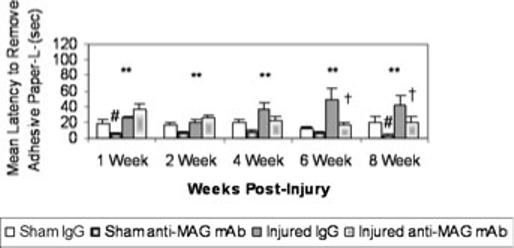
Latency to remove adhesive paper from left forepaw (mean + SEM). Following injury, brain-injured IgG-treated animals had significantly longer latencies to remove the sticky paper from the left forepaw than sham-injured IgG-treated animals (**P < 0.01). At 1 and 8 weeks post-surgery sham animals given anti-myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) monoclonal antibody (mAb) had significantly shorter latencies to remove the paper than their IgG-treated counterparts (#P < 0.05). At 6 and 8 weeks post-injury, brain-injured animals treated with anti-MAG mAb were able to remove the paper significantly faster than their IgG-treated counterparts (†P < 0.05).
