Fig. 5.
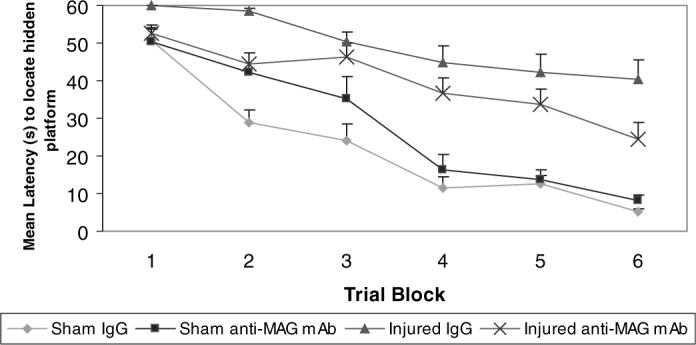
Learning at 6 weeks post-injury. Latencies to reach the hidden platform using the Morris water maze paradigm to assess visuospatial learning at 6 weeks post-injury (means + SEM). Brain-injured vehicle-treated animals had significantly longer latencies to reach the platform when compared with sham-injured, IgG-treated controls (P < 0.001). Treatment with the anti-myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) monoclonal antibody (mAb) following lateral fluid percussion brain injury resulted in consistently shorter latencies compared with IgG-treated brain-injured controls but this did not reach statistical significance (P = 0.094).
