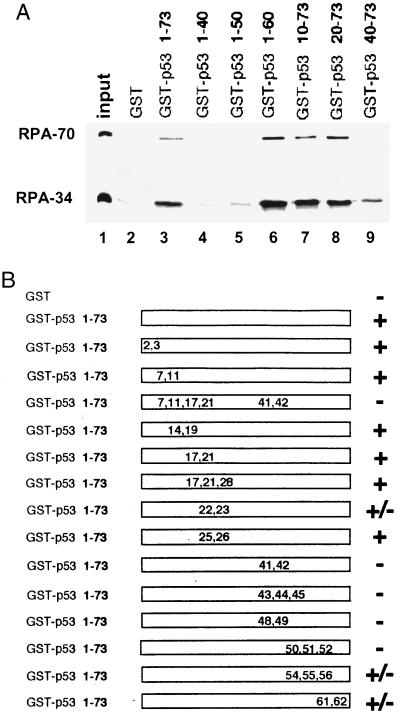
Figure 1.
Characterization of the RPA-interacting domain of p53. (A). Deletion analysis of the N-terminal domain of p53. One-fourth of the input purified RPA (50 ng) and 40% of the bound fractions were loaded on the gel. Approximately 25–30% of the input RPA was bound to the wild-type GST–p53 beads. (B) RPA-binding ability of various point mutants of the p53 activation domain. +, Affinity no less than the wild type; −, signal equivalent to GST alone; ±, reduced binding affinity similar to the one shown in Fig. 1A, lane 9. The positions and types of these mutations are E2K, E3K, D7H, E11K, L14Q, E17K, F19S, D21H, L22Q, W23S, L25Q, L26H, E28K, D41H, D42H, L43A, M44A, L45A, D48H, D49H, I50A, E51A, Q52A, F54A, T55A, E56A, D61H, and E62K.