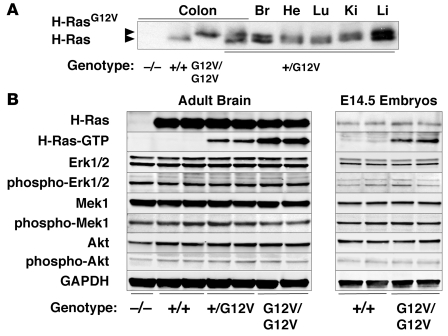
Figure 1. Functional characterization of the H-Ras signaling pathway in H-RasG12V adult brain and E14.5 embryos.
(A) Western blot analysis of the expression levels of wild-type H-Ras+/+ and mutant H-RasG12V proteins. Protein extracts (200 μg) derived from colons of H-Ras+/+, H-Ras+/G12V, H-RasG12V/G12V, and H-Ras–/– mice as well as from brain (Br), heart (He), lung (Lu), kidney (Ki), and liver (Li) of H-Ras+/G12V animals were subjected to Western blot analysis. In the case of brain, only one-fourth of the sample was loaded. Migration of the wild-type H-Ras and mutant H-RasG12V proteins is indicated by arrowheads. (B) Protein extracts (40 μg) from the indicated genotypes obtained from 2-month-old adult brains and E14.5 whole embryos were resolved by SDS-PAGE, transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane, and blotted with antibodies against H-Ras and the nonphosphorylated and phosphorylated forms of Erk1/2, Mek1, and Akt. Levels of active H-Ras protein bound to GTP (H-Ras–GTP) were determined by its ability to interact with the Ras binding domain of c-Raf. GAPDH was used as loading control.