Abstract
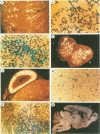
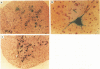
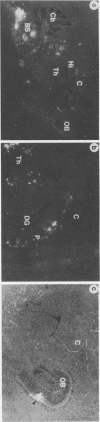
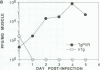
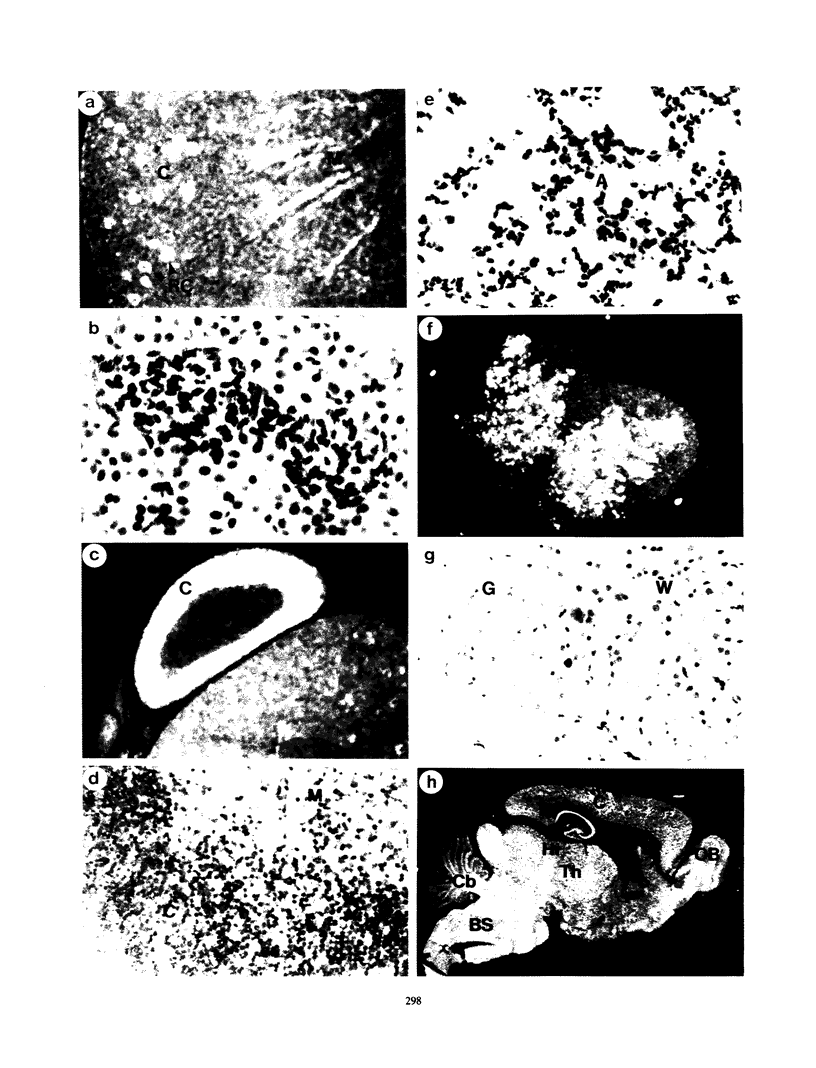
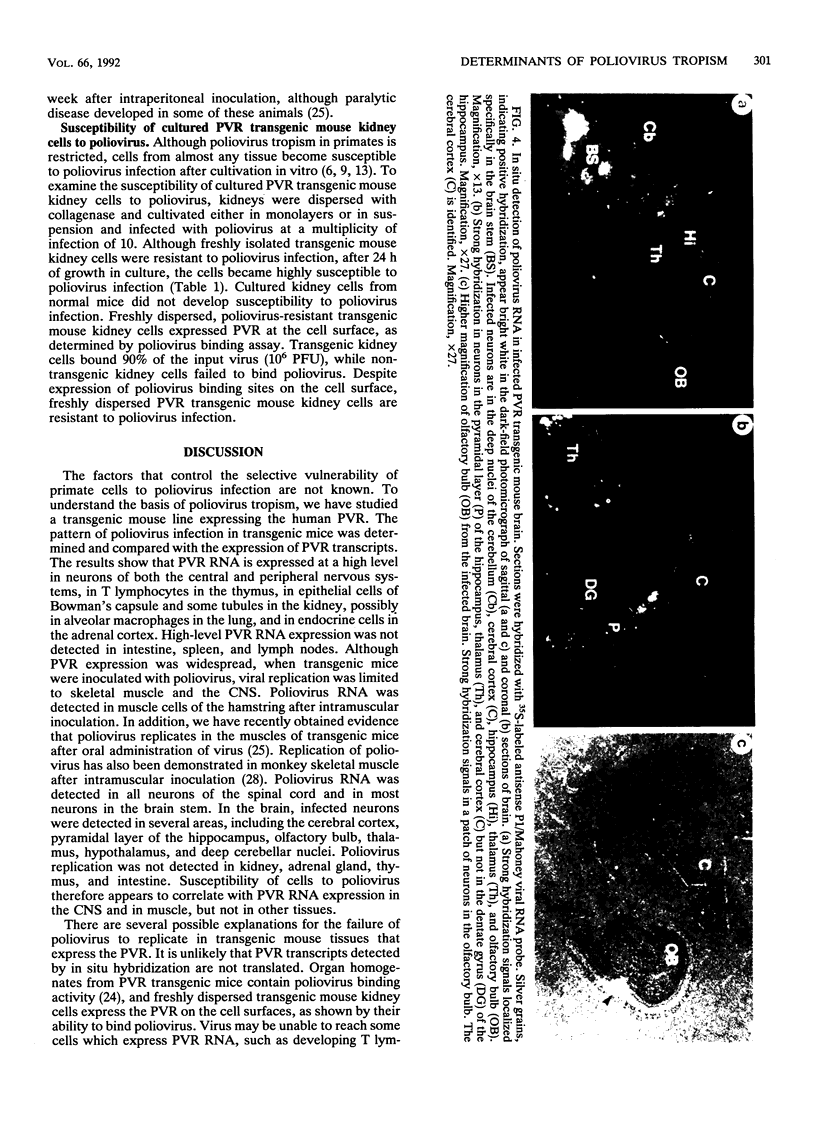
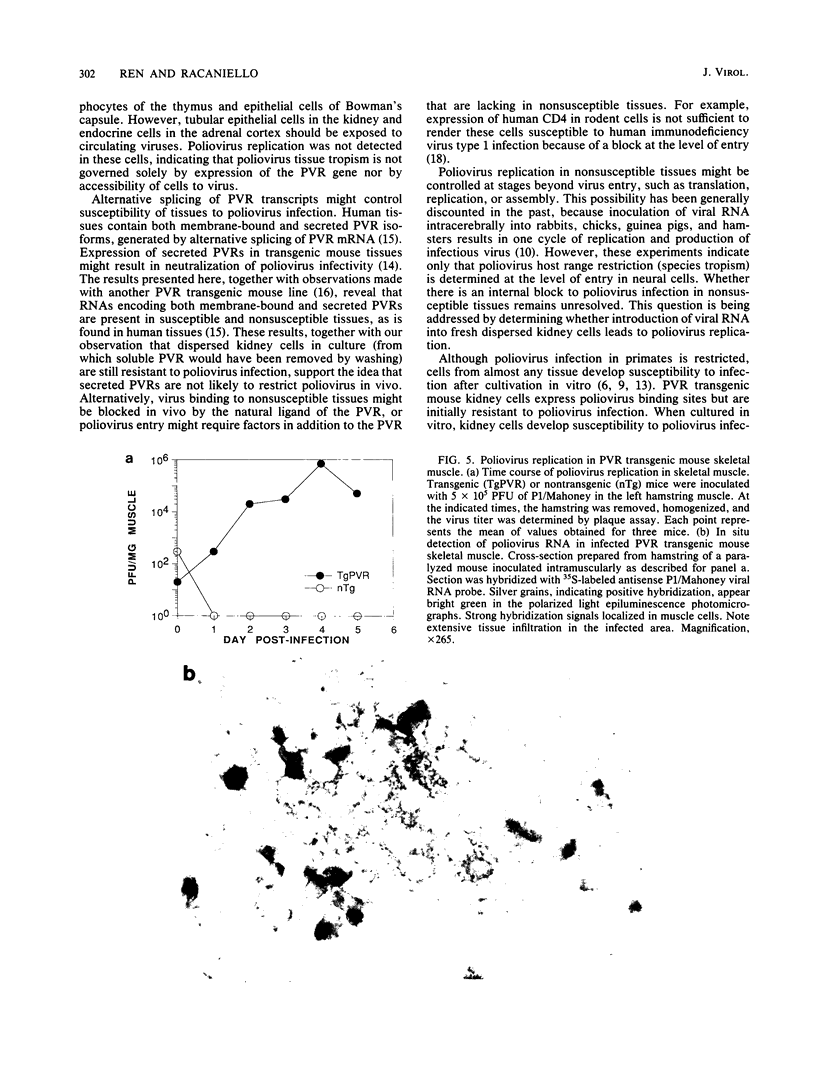
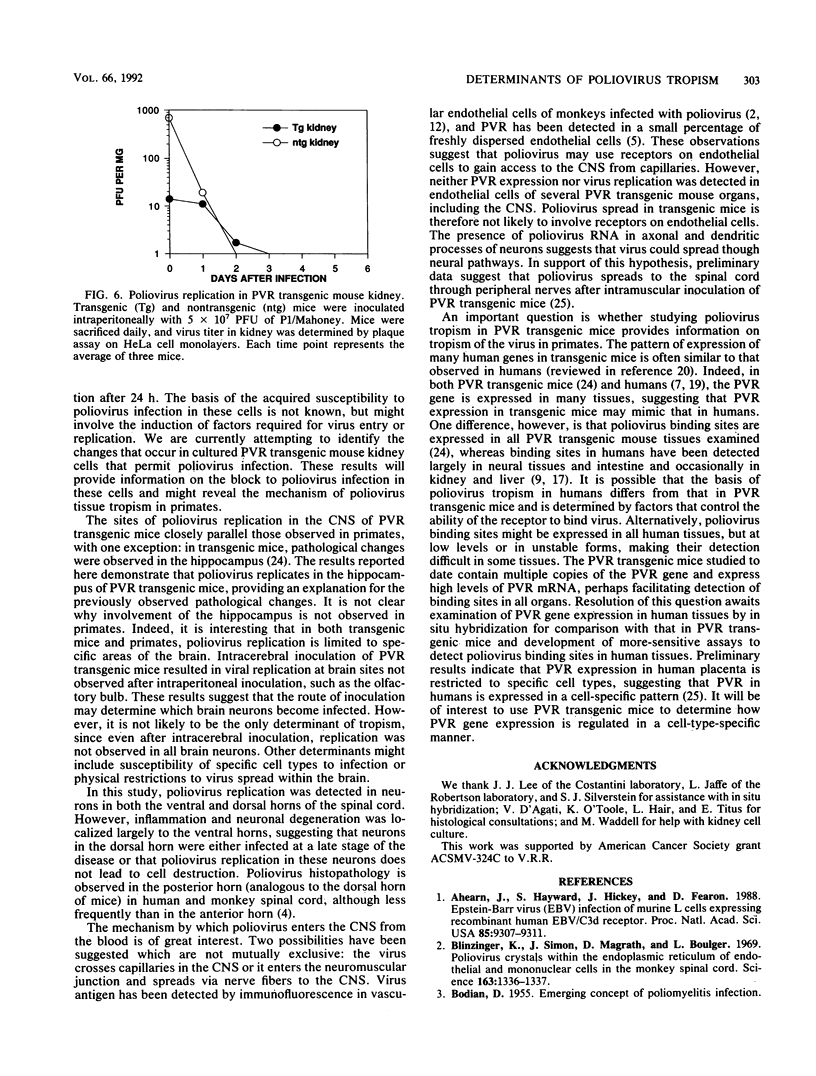
Expression of the human poliovirus receptor (PVR) in transgenic mice results in susceptibility to poliovirus infection. In the primate host, poliovirus infection is characterized by restricted tissue tropism. To determine the pattern of poliovirus tissue tropism in PVR transgenic mice, PVR gene expression and susceptibility to poliovirus infection were examined by in situ hybridization. PVR RNA is expressed in transgenic mice at high levels in neurons of the central and peripheral nervous system, developing T lymphocytes in the thymus, epithelial cells of Bowman's capsule and tubules in the kidney, alveolar cells in the lung, and endocrine cells in the adrenal cortex, and it is expressed at low levels in intestine, spleen, and skeletal muscle. After infection, poliovirus replication was detected only in neurons of the brain and spinal cord and in skeletal muscle. These results demonstrated that poliovirus tissue tropism is not governed solely by expression of the PVR gene nor by accessibility of cells to virus. Although transgenic mouse kidney tissue expressed poliovirus binding sites and was not a site of poliovirus replication, when cultivated in vitro, kidney cells developed susceptibility to infection. Identification of the changes in cultured kidney cells that permit poliovirus infection may provide information on the mechanism of poliovirus tissue tropism.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahearn J. M., Hayward S. D., Hickey J. C., Fearon D. T. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection of murine L cells expressing recombinant human EBV/C3d receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9307–9311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinzinger K., Simon J., Magrath D., Boulger L. Poliovirus crystals within the endoplasmic reticulum of endothelial and mononuclear cells in the monkey spinal cord. Science. 1969 Mar 21;163(3873):1336–1337. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3873.1336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couderc T., Barzu T., Horaud F., Crainic R. Poliovirus permissivity and specific receptor expression on human endothelial cells. Virology. 1990 Jan;174(1):95–102. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90058-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enders J. F., Weller T. H., Robbins F. C. Cultivation of the Lansing Strain of Poliomyelitis Virus in Cultures of Various Human Embryonic Tissues. Science. 1949 Jan 28;109(2822):85–87. doi: 10.1126/science.109.2822.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freistadt M. S., Kaplan G., Racaniello V. R. Heterogeneous expression of poliovirus receptor-related proteins in human cells and tissues. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5700–5706. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh B., Ogasawara T., Toyoda T., Inocencio N. M., Hamaguchi M., Nagai Y. An endoprotease homologous to the blood clotting factor X as a determinant of viral tropism in chick embryo. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):4189–4195. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07643.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J., McLAREN L. C., SYVERTON J. T. The mammalian cell-virus relationship. IV. Infection of naturally insusceptible cells with enterovirus ribonucleic acid. J Exp Med. 1959 Jul 1;110(1):65–80. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J. Receptor affinities as major determinants of enterovirus tissue tropisms in humans. Virology. 1961 Nov;15:312–326. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90363-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe L., Jeannotte L., Bikoff E. K., Robertson E. J. Analysis of beta 2-microglobulin gene expression in the developing mouse embryo and placenta. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3474–3482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN A. S. Comparison of susceptible and resistant cells to infection with poliomyelitis virus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1955 Sep 27;61(4):830-8; discussion, 838-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1955.tb42539.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNIN C. M., JORDAN W. S., Jr In vitro absorption of poliovirus by noncultured tissues. Effect of species, age and malignancy. Am J Hyg. 1961 May;73:245–257. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanamitsu M., Kasamaki A., Ogawa M., Kasahara S., Imamura M. Immunofluorescent study on the pathogenesis of oral infection of poliovirus in monkeys. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1967 Apr;20(2):175–194. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.20.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Freistadt M. S., Racaniello V. R. Neutralization of poliovirus by cell receptors expressed in insect cells. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4697–4702. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4697-4702.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike S., Horie H., Ise I., Okitsu A., Yoshida M., Iizuka N., Takeuchi K., Takegami T., Nomoto A. The poliovirus receptor protein is produced both as membrane-bound and secreted forms. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3217–3224. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07520.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike S., Taya C., Kurata T., Abe S., Ise I., Yonekawa H., Nomoto A. Transgenic mice susceptible to poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):951–955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., Dalgleish A. G., McDougal J. S., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., Axel R. The T4 gene encodes the AIDS virus receptor and is expressed in the immune system and the brain. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):333–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90590-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn C. L., Wimmer E., Racaniello V. R. Cellular receptor for poliovirus: molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of a new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):855–865. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90690-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Germ-line transformation of mice. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:465–499. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.002341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Baltimore D. Cloned poliovirus complementary DNA is infectious in mammalian cells. Science. 1981 Nov 20;214(4523):916–919. doi: 10.1126/science.6272391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Meriam C. Poliovirus temperature-sensitive mutant containing a single nucleotide deletion in the 5'-noncoding region of the viral RNA. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):498–507. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90211-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R. Poliovirus neurovirulence. Adv Virus Res. 1988;34:217–246. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60519-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren R. B., Costantini F., Gorgacz E. J., Lee J. J., Racaniello V. R. Transgenic mice expressing a human poliovirus receptor: a new model for poliomyelitis. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):353–362. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90168-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABIN A. B. Pathogenesis of poliomyelitis; reappraisal in the light of new data. Science. 1956 Jun 29;123(3209):1151–1157. doi: 10.1126/science.123.3209.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WENNER H. A., KAMITSUKA P. Primary sites of virus multiplication following intramuscular inoculation of poliomyelitis virus in cynomolgus monkeys. Virology. 1957 Jun;3(3):429–443. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. G., Rott R. Influenza virus A pathogenicity: the pivotal role of hemagglutinin. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):665–666. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90321-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zack J. A., Arrigo S. J., Weitsman S. R., Go A. S., Haislip A., Chen I. S. HIV-1 entry into quiescent primary lymphocytes: molecular analysis reveals a labile, latent viral structure. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):213–222. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90802-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]