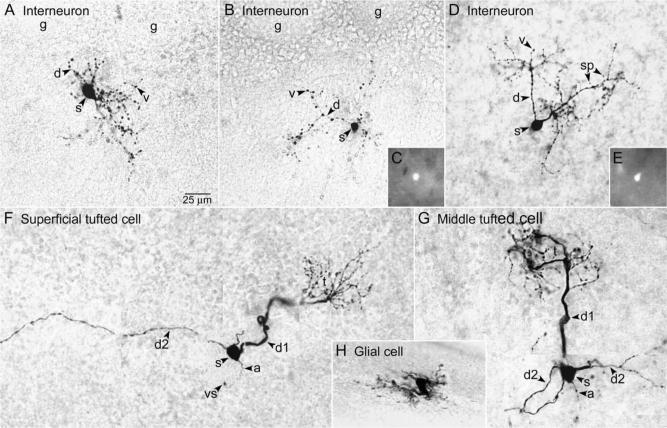
Fig. 1.
Morphological characteristics of cells in the EPL of C57BL/6J mice (A and F–H) and GAD65-GFP mice (B–E). Single sections (A–E and H) or montages (F and G) illustrate the cell body (s, soma), major portion of the dendritic tree, and axon (a, if present). (A, B) The dendrites (d) of superficial interneurons located near the GL bridged the EPL space below several adjacent glomeruli (g). The d had numerous varicosities (v), and some had sparse spines (sp, Fig. 1D). (C) Epifluorescence image of GFP in the soma of the cell shown in Fig. 1B, in the unfixed slice. (D) An interneuron exhibiting similar characteristics located deeper in the EPL. Two major d extended toward the GL. (E) Epifluorescence image of GFP in the soma of the cell shown in Fig. 1D. (F) Superficial tufted cell with short primary d (d1) giving rise to a glomerular tuft (t) and long secondary d (d2) extending laterally in the EPL. (G) Middle tufted cell with d1 giving rise to a t and multiple d2 extending laterally in the EPL. (H) Astrocyte.