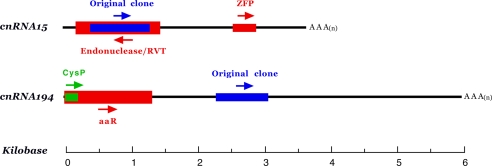
Fig. 2.
Structural analysis of cnRNAs 15 and 194. Sense and antisense strands are defined by the orientation of the 5′ caps and 3′ polyadenylation sites. Blue bars represent the 692- and 671-nt sequences originally cloned from isolated centrosomes; arrows indicate 5′ to 3′ orientation. cnRNA15 includes a 314-nt putative protein coding domain (red) with 85% identity at the amino acid level to a newly described Spisula zinc finger protein (ZFP; GenBank accession no. AB231865). The homology domain in cnRNA15 does not correspond to the C2H2 zinc-binding motif region. In addition, a 1,128-nt domain is present in the antisense strand that exhibits 40% identity (at the amino acid level) to S. purpuratus endonuclease/RVT (GenBank accession no. XP792610). An amino acid-binding domain similar to that found in glutamate receptors and other amino acid-binding proteins from a variety of species is present in the 5′ end of cnRNA194, overlapping with a cathepsin-like cysteine protease (CysP) protease domain (green) [GenBank accession nos. EU069824 (cnRNA15) and EU069825 (cnRNA194).]