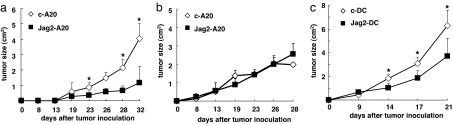
Fig. 4.
Inoculation of Jag2-A20 cells enables NK cells to kill A20 cells transplanted at a different site. (a) Jag2-A20 and A20 cells (closed squares) or c-A20 and A20 cells (open diamonds) were inoculated in different sites of the same SCID mouse (n = 5), and the tumor size of the A20 cells was monitored. The tumor size was calculated as (axial) × (horizontal) diameter. Data are shown as the mean ± SD. *, statistical significance (P < 0.05). These results are representatives of three independent experiments. (b) SCID mice (n = 5) injected with Jag2-A20 and A20 cells (filled squares) or c-A20 and A20 cells (open diamonds) were treated with 100 μg of anti-asialo-GM1 antibody (day −1, day 2, day 5, day 8; n = 5), and the tumor size of the A20 cells was monitored. Tumor size was calculated as (axial) × (horizontal) diameter. Data are shown as the mean ± SD. *, statistical significance (P < 0.05). These results are representatives of three independent experiments. (c) A20 cells were inoculated with DC transduced with Jagged2 (filled squares) or control vector (open diamonds) in SCID mice, and the tumor size of A20 cells was monitored. The tumor size was calculated as (axial) × (horizontal) diameter. Data are shown as the mean ± SD. *, statistical significance (P < 0.05). These results are representatives of three independent experiments.