Fig. 1.
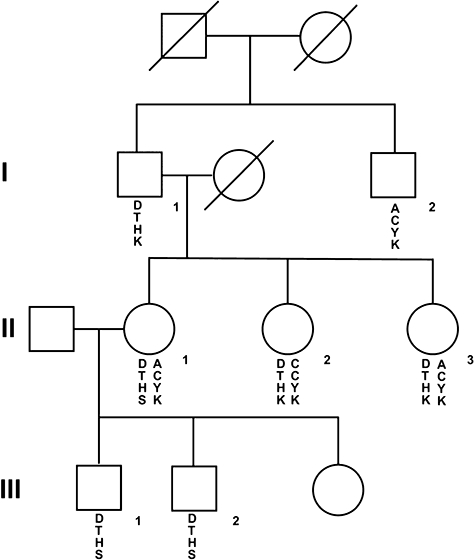
The pedigree for a family with two different alterations in Btk is shown. Squares represent males and circles indicate females. Genetic markers in and near Btk are shown below the symbol for each individual. The top marker is the highly polymorphic marker DXS101, which is 700 kb 5′- to Btk; the second marker is the uncommon polymorphism in intron 2 of Btk, the third marker is the alteration in codon 418 giving rise to a histidine (H) rather than the wild-type tyrosine (Y). The fourth marker is the alteration in codon 625 giving rise to a premature stop codon (S) rather than the wild-type lysine (K).
