Fig. 1.
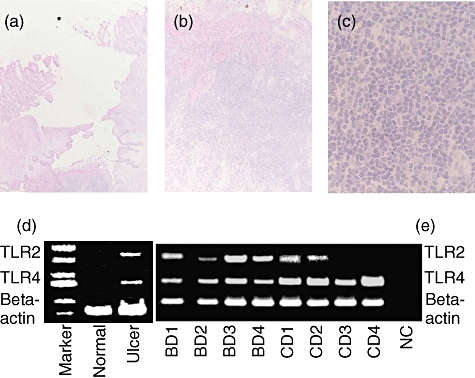
Histological examination and reverse transcription– polymerase chain reaction (RT–PCR) analysis of the intestinal lesions of Behçet's disease (BD). (a) Haematoxylin and eosin staining of an intestinal lesion of BD. An intestinal ulcer of BD was infiltrated by inflammatory cells. Results of a representative case of BD are shown. Magnification, × 2. (b) Higher magnification of (a). Most mononuclear cells. A very small number of neutrophils also infiltrated the site. Magnification, × 10. (c) Higher magnification of the (a). Magnification ×100. (d) RT–PCR analysis of Toll-like receptor (TLR) mRNA expression of the intestinal lesion of BD. TLR-2 and TLR-4 mRNA expressions were analysed. As control diseases, intestinal lesions of patients with Crohn's disease (CD) were included. NC, negative control (DDW).
