Fig. 1.
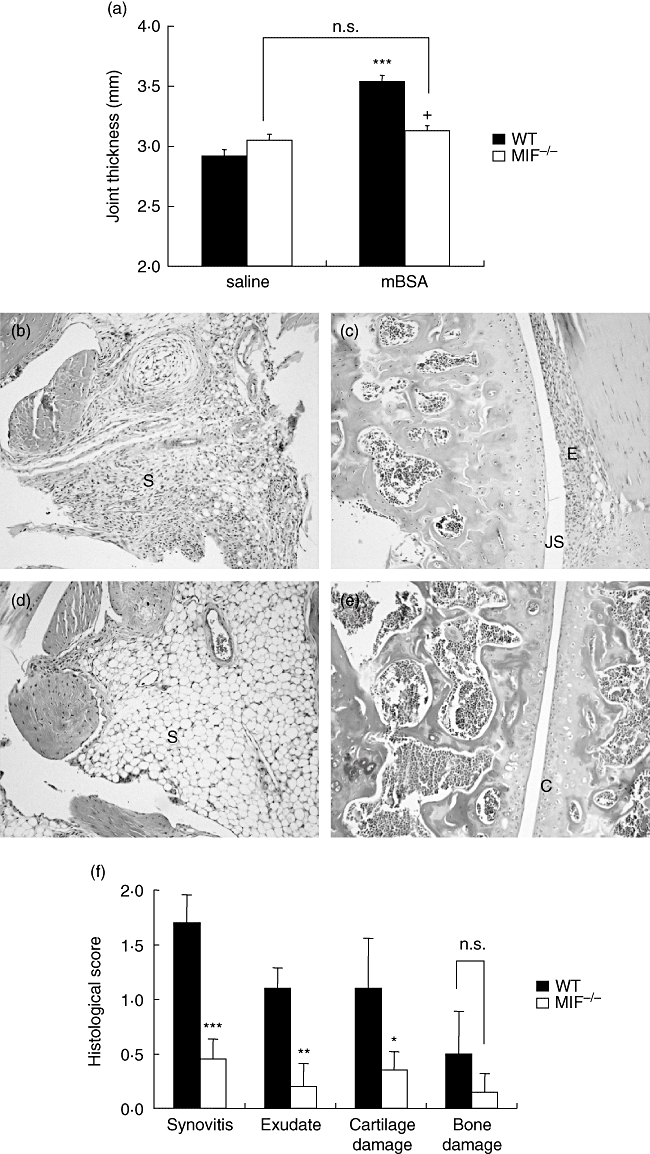
Arthritis induction in migration inhibitory factor (MIF)−/−and wildtype (WT) mice. Mice received intra-articular injections of methylated bovine serum albumin (mBSA) (30 μg; test knee) or saline (control knee) on day 21 after first immunization. On day 28, arthritis severity was measured by thickness of mBSA- and saline-injected knee joints (a) WT, but not MIF −/− mice, exhibited significantly increased joint thickness in response to mBSA (***P < 0·001). MIF −/− mice joint thickness after mBSA injection was significantly lower than WT (+P < 0·0001). Histological scores (f) of Safranin-O-stained joint sections on a scale of 0–3 for each individual feature, synovitis, joint space exudate, cartilage degradation and bone damage (as described in Materials and Methods). WT mice (b and c) exhibited more severe arthritis in comparison with MIF −/− mice (d and e) as evidenced by significantly higher scores for all but one histopathological feature (f) (*P < 0·05, **P < 0·01, ***P < 0·001 for MIF −/−versus WT mice). S = synovium, JS = joint space, E = exudate, C = articular cartilage. Magnification ×200. n.s., not significant.
