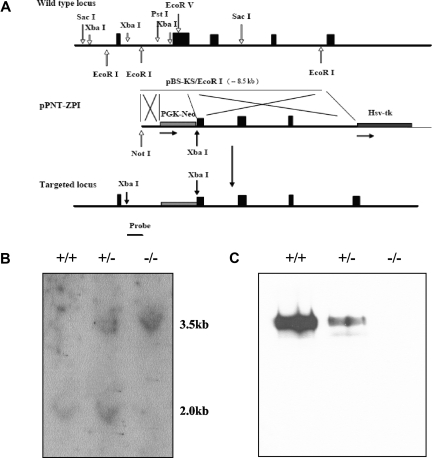
Figure 1.
ZPI gene disruption in mice. (A) The targeting construct (middle) contains a PGK-Neo cassette that replaces DNA fragment between the Pst 1 site in intron A and the EcoRV site in exon 2, thereby removing the ZPI DNA that encodes the signal peptide and N-terminus of ZPI, and inducing a frame-shift mutation. An HSV-TK cassette was added at the 3′-end of the construct to permit negative selection. The targeting vector was linearized with Not 1 and introduced into 129/Sv-derived RW4 ES cells by electroporation and stable transfectants were selected using G418 and gancyclovir. The predicted product of homologous recombination is shown at the bottom. The position of the 673 bp hybridization probe used to detect successful gene targeting is also depicted. (B) Southern blot analysis. Genomic DNA prepared from tail biopsies was analyzed by restriction digestion with Xba1 and hybridization with the probe. (C) Western blot analysis of ZPI in mouse plasma. SDS-PAGE (10%) and Western blotting of mouse plasma (5 μL of a 1:10 dilution) with rabbit antihuman ZPI polyclonal antibodies.