Figure 2.
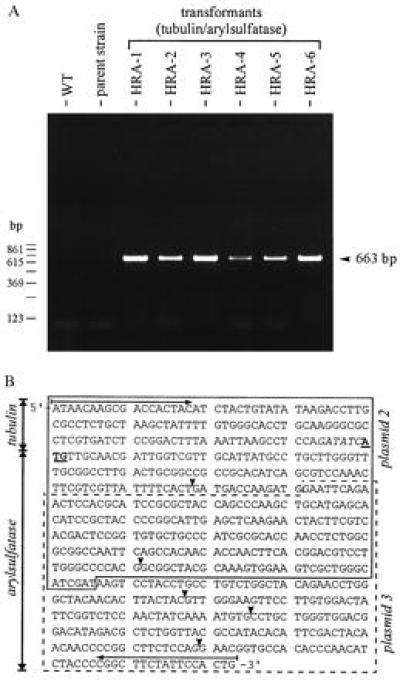
(A) RT and subsequent PCR amplification of the chimeric mRNA. RNA was extracted from 20 Volvox spheroids of parent strain 153–48, wild-type algae (WT), or the six transformants constitutively expressing the arylsulfatase gene (HRA-1 through HRA-6). Sizes of PCR products (663 bp) were determined by using a 123-bp ladder as size marker and by DNA sequencing. (B) Sequence of cDNA (663 bp) obtained from RT and subsequent PCR amplification of the overlap region of the tubulin/arylsulfatase gene from Volvox clones HRA-1 through HRA-6. All clones resulted from transformation experiments using a mixture of plasmids 2 and 3 (and nitA as a selection marker). The sequence stretch contributed by plasmid 2 is boxed with a solid line; the contribution of plasmid 3 is boxed with a dashed line. The translation initiation site (ATG) is highlighted (shown underlined and in boldface type). The artificial EcoRV restriction site in front of the translation initiation site, shown in italic type, separates the β-tubulin sequence from the arylsulfatase sequence. Introns were spliced correctly. The positions of the introns within this cDNA-fragment are indicated by solid arrowheads. PCR primers used are indicated by horizontal arrows.
