Figure 3.
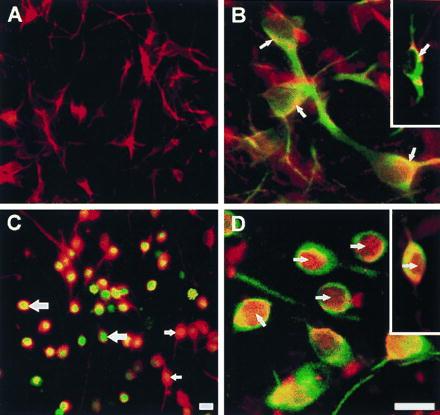
ROS-induced DCDHF fluorescence and translocation of NF-κB in ceramide-treated primary cultures of mesencephalon. (A) Neurons in untreated cultures, identified by rhodamine (red) immunofluorescence with an antibody against MAP-2. (B) NF-κB in untreated cultures, identified by rhodamine (red) immunofluorescence in neurons (arrows) is preferentially localized in the cytoplasm, and appears yellow because of superimposition with fluorescein (green) MAP-2 or tyrosine hydroxylase (Inset) immunoreactivity. (C) ROS-activated DCDHF green fluorescence that appears orange/yellow/green due to superimposition on red MAP-2 staining in neurons in cultures treated with 25 μM C2-ceramide for 5 hr. (D) NF-κB (red) labeling is primarily in the nuclei (arrows) of green MAP-2 and tyrosine hydroxylase-immunolabeled neurons in ceramide-treated cultures (Inset). [Bar = 20 μm (30 μm for Insets)].
