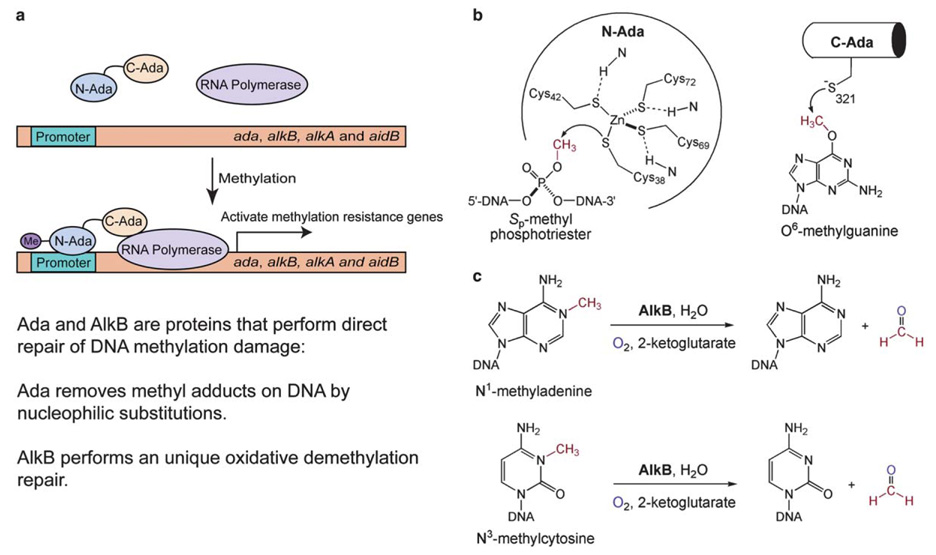
Fig. 1.
Schematic representations of the direct repair of methylation DNA damage in E. coli by proteins in the ada operon. (a) E. coli Ada is a transcriptional activator that senses methylation challenge and activates its own expression and three other genes, alkB, alkA and aidB. AlkA is a glycosylase that cleaves methylated bases from DNA. The function of AidB is still unknown. Both Ada and AlkB perform direct repair of methylation (alkylation) DNA damage. (b) Ada uses Cys residues to nucleophilically remove methyl groups from DNA backbone and bases. (c) AlkB catalyzes an oxidative dealkylation repair of DNA base lesions.