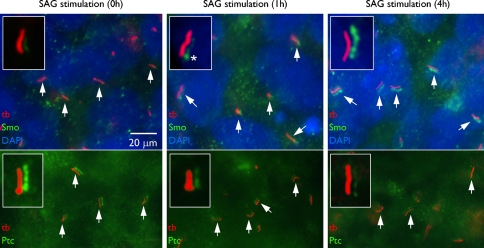
Fig. 2.
Primary cilia of human embryonic stem cells. Immunofluoresence microscopy using acetylated α tubulin antibody (tb) reveals the presence of primary cilia (arrows) on human embryonic stem cells. In the absence of stimulation, the hedgehog receptor ‘patched’ (Ptc) colocalizes with the acetylated α tubulin all along the ciliary membrane. Red and green channels are displaced in the images to define colocalization more clearly. Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). Upon stimulation, as part of the signaling cascade, Ptc leaves the cilium and the smoothened receptor (Smo) enters to activate the hedgehog signaling cascade. Asterisk marks the ciliary base. (From Kiprilov et al. 2008, with permission, courtesy of The Journal of Cell Biology)