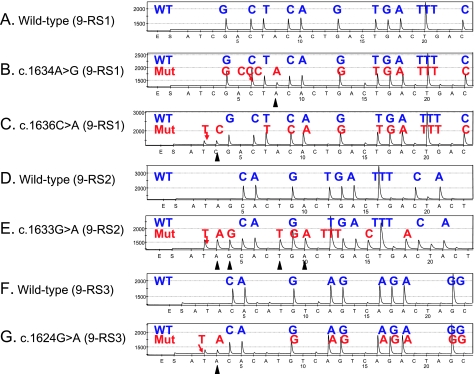
Figure 2.
PIK3CA exon 9 Pyrograms (antisense strand). (A) Wild type exon 9 by the 9-RS1 primer. (B) The c.1634A>G mutation (arrow) causes a shift in reading frame and results in a new peak at A (arrowhead), which serves as quality assurance. (C) The c.1636C>A mutation (arrow) causes a shift in reading frame and results in a new peak at C (arrowhead), which serves as quality assurance. (D) Wild type exon 9 by the 9-RS2 primer. (E) The c.1633G>A mutation (arrow) causes a shift in reading frame and results in new peaks (arrowheads), which serves as quality assurance. (F) Wild type exon 9 by the 9-RS3 primer. (G) The c.1624G>A mutation (arrow) causes a shift in reading frame and results in a new peak at A (arrowhead), which serves as quality assurance. Mut indicates mutant; WT, wild type.