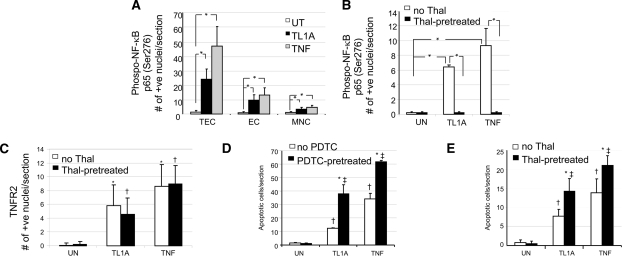
Figure 4.
Quantitative analysis of nuclear P-S276-p65 expression, TNFR2, and TUNEL in human kidney organ cultures. (A) Addition of TL1A or TNF significantly increased nuclear P-S276-p65 expression in TEC, EC, and MNC, with staining predominantly in TEC. *P < 0.01. (B) Thalidomide pretreatment abolished the rise in nuclear P-S276-p65 expression induced by either TL1A or TNF. *P < 0.01. (C) However, thalidomide did not block the significant increase in the TL1A- or TNF-induced expression of TNFR2 in TEC. *P < 0.01 TL1A or TNF versus untreated; †P < 0.01 TL1A or TNF versus untreated all with Thal. (D and E) TUNEL-positive TEC with apoptotic morphology were counted in 10 fields of view in six (D) or two (E) different experiments. A significant increase in apoptosis was observed in TL1A- or TNF-treated cultures compared with controls, which increased further in cultures treated with PDTC or thalidomide as compared with cultures without PDTC or thalidomide (in all 10 fields were analyzed in 6 or 2 [E] experiments). In panel D, *P < 0.01 PDTC pre-treatment versus no PDTC; †P < 0.01 TL1A or TNF versus untreated; and ‡P < 0.01 TL1A or TNF versus untreated all with Thal. In panel E, *P < 0.01 Thal pre-treatment versus no Thal; †P < 0.01 TL1A or TNF versus untreated; and ‡P < 0.01 TL1A or TNF versus untreated all with Thal. ANOVA P < 0.001; post hoc Tukey's Honestly Significantly Different; P < 0.01.