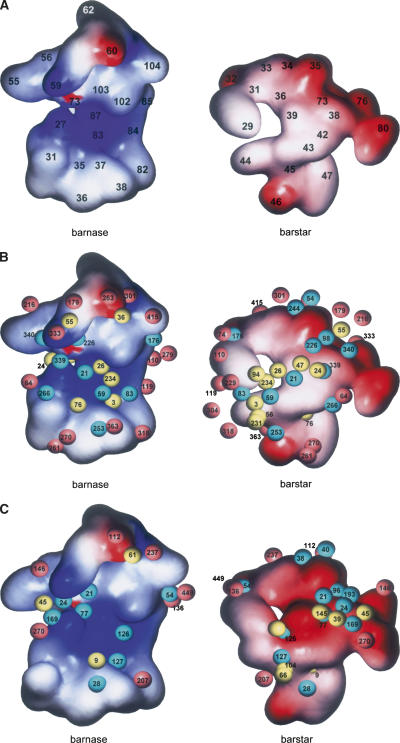
Figure 2.
Potential surfaces of the interface of the bn–bs complex. This interface comprises 20 residues of bn (Lys27, Gln31, Trp35, Val36, Ala37, Ser38, Ile55, Phe56, Arg59, Glu60, Lys62, Glu73, Phe82, Arg83, Asn84, Ser85, Arg87, His102, Tyr103, and Gln104) and 16 residues of bs (Tyr29, Gly31, Asn33, Leu34, Asp35, Ala36, Trp38, Asp39 [Ala39], Thr42, Gly43, Trp44, Val45, Glu46, Tyr47, Val73, and Glu76). (A) Potential surfaces of the interface of the mutant complex without hydrated water molecules. The number written on the surface represents the number of amino acid residues of bn or bs. (B,C). Potential surfaces of the interface of the mutant (B) or wild-type (C) complex with hydrated water molecules. (Magenta spheres) “Edge” water molecules, (yellow spheres) “buried” water molecules, (cyan spheres) “bridging” water molecules. The number written on the spheres represents the number of the hydrated water molecule referred to in Supplemental Table 5. Surface color-coded according to electrostatic potential calculated by the Poisson-Boltzmann solver within GRASP2 and displayed within GRASP2 (Petrey and Honig 2003).