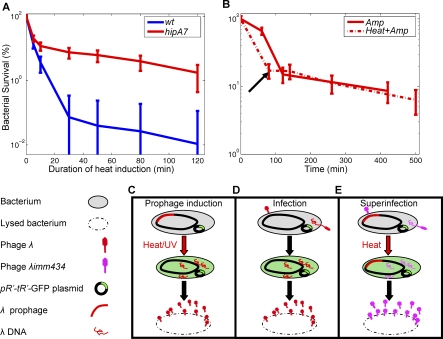
Figure 1. High Persistence in the Response to Prophage Heat Induction.
(A) Cultures of wt and hipA7 λcI857KnR lysogenic bacteria were subjected to heat (42 °C) to trigger prophage induction. The survival percentages are plotted versus the duration of exposure to heat. The killing curves show the bimodal behavior characteristic of persistence, with the hipA7 persistence level far above the wt.
(B) Persisters to prophage heat induction persist ampicillin (Amp) treatment: Killing curves in ampicillin of hipA7 λcI857KnR lysogenic bacteria (solid line) and of persisters to 80-min prophage heat induction (dashed line). Arrow shows the time of transition from heat induction to ampicillin exposure. The two curves are similar, showing that persisters to prophage heat induction are also persistent to ampicillin.
Error bars represent the standard deviation between triplicates. Similar results were obtained in at least three independent experiments.
(C–E) Schematic layout of host–phage systems used in this work (C) Prophage induction of λcI857KnR lysogens by heat, or of λc+KnR by UV. (D) Infection by λcI60. (E) Heat-induced λcI857KnR lysogens superinfected with λimm434cI3003 phages.