Fig. 2.
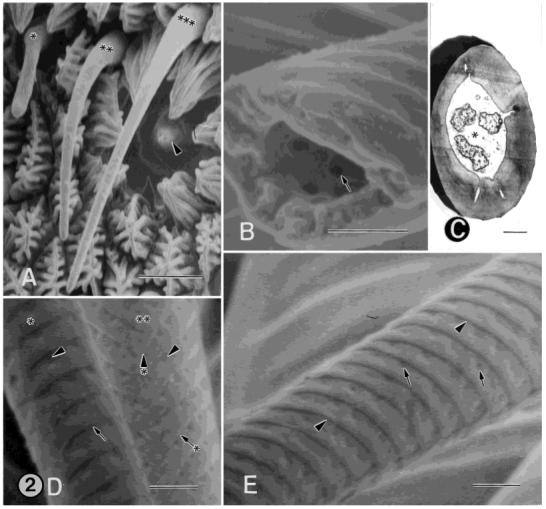
A: SEM of female annulus showing four different sensillum types in close proximity to one another. Asterisk, type-B basiconic sensilllum; double asterisks, type-A basiconic sensillum; triple asterisks, type-A trichoid sensillum; arrowhead, type-A coeloconic sensillum. B: SEM of the middle portion of the cuticular shaft from a type-A trichoid, single-walled, multiporous sensillum that is broken. This view shows the interior of the cuticular shaft. Three pores (one denoted by the arrow) are visible. The pores extend through the full thickness of the shaft and are visible on the exterior wall of the sensillum, shown in D and E. C: TEM of a cross-section of a type-B trichoid sensillum showing three unbranched distal dendrites surrounded by the sensillar sinus (asterisk). D: SEM showing the middle portion of the cuticular shafts from a type-A (asterisk) and type-B (double asterisks) trichoid sensillum. The shaft of the type-A sensillum bears circumferential, cuticular ridges (arrow), which form a helical pattern over the basal quarter of its length and a more circular pattern over the remaining length of the sensillum. The shaft of the type-B sensillum bears diagonal, cuticular ridges (arrow with asterisk), forming a herringbone pattern. The ridges fuse together on one side along the length of the sensillum (arrowhead with asterisk). In both sensillum types, the shafts are perforated by pores (arrowheads). The pores are located in cuticular depressions that extend to the tip of the sensillum and are arranged in a single row along the distal margin of the ridges. E: SEM of the middle portion of the cuticular shaft from a type-A trichoid sensillum. Arrowheads, cuticular ridges; arrows, pores. Scale bars = 5 μm in A, 0.5 μm in B-E.
