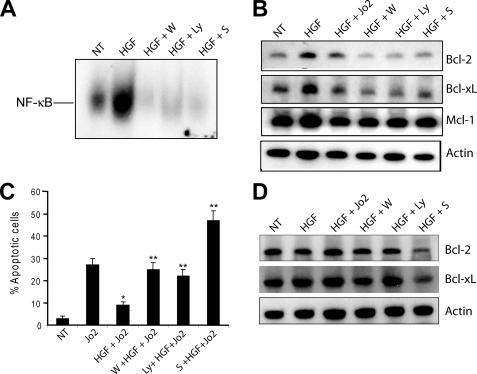
FIGURE 3.
NF-κB activation is required for the antiapoptotic effects of HGF in Cre-Ctrl hepatocytes. A, electromobility shift assays of NF-κB DNA binding activity. Cre-Ctrl hepatocytes were pretreated with 100 μm wortmannin (W), 50 μm LY294002 (Ly), and 100 μm sulfasalazine (S) for 30 min followed by 40 ng/ml HGF for 12 h. Results were confirmed in three independent experiments. B, expression of antiapoptotic proteins in Cre-Ctrl cells. Cells were pretreated with 100 μm wortmannin, 50 μm LY294002, and 100 μm sulfasalazine for 30 min followed by 40 ng/ml HGF for 12 h. C, effect of inhibition of PI3K/Akt and NF-κB on frequency of apoptosis. After 16 h of serum starvation, cells were pretreated with 100 μm wortmannin, 50 μm LY294002, or 100 μm sulfasalazine for 30 min followed by treatment with HGF (40 ng/ml) for 12 h and Jo2 (0.5 μg/ml) for the last 6 h in culture. Apoptotic index was detected by counting apoptotic cells after PI staining. Each column represents the mean ± S.E. At least 500 nuclei were counted from duplicate slides from three independent cultures. D, expression of antiapoptotic proteins in Met-KO cells. Cells were pretreated with 100 μm wortmannin, 50 μm LY294002, and 100 μm sulfasalazine for 30 min followed by 40 ng/ml HGF for 12 h. A representative Western blot of three experiments is shown in B and D.*, p < 0.05 against Jo2 treatment alone; **, p < 0.05 against HGF + Jo2 treatment. NT, no treatment.