Fig. 3. Effect of melatonin on depression-like behavior.
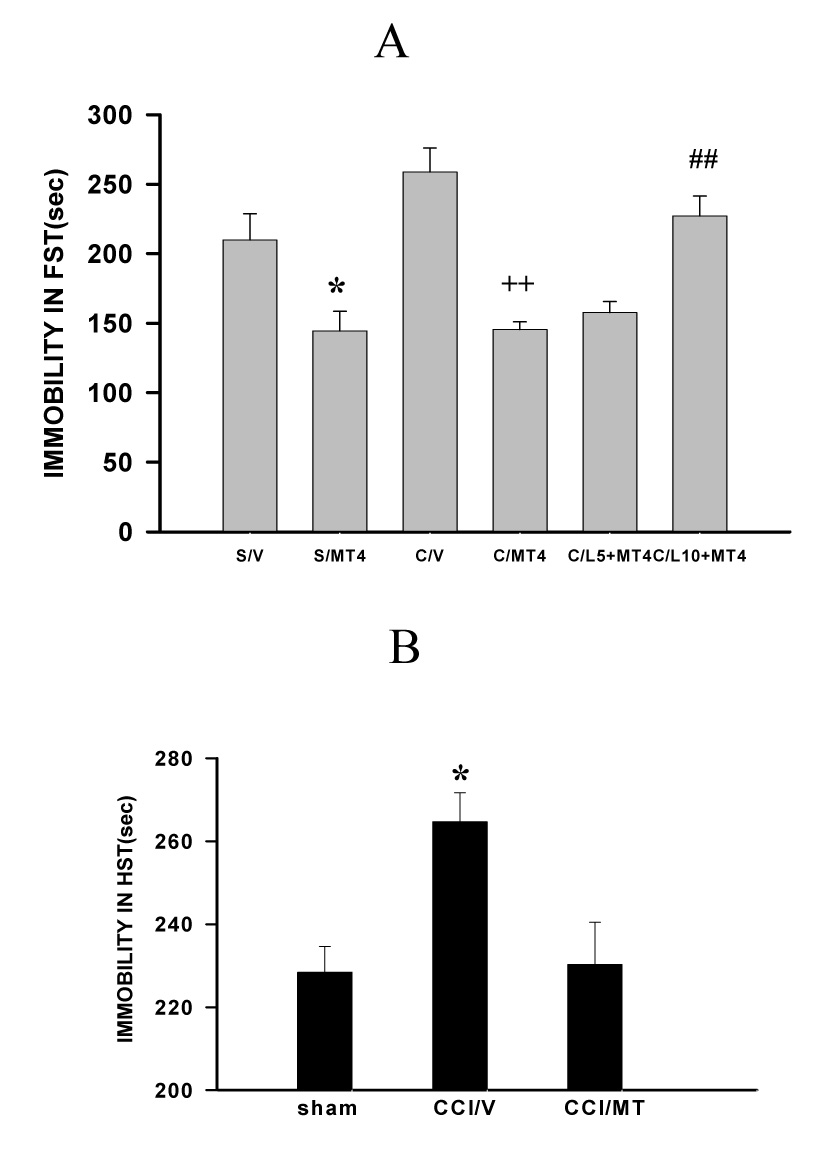
A: When examined on postoperative day 7, the immobility time in the forced swimming test (FST) in WKY rats was significantly improved by melatonin (MT, 4 µg, once daily × 7 days) administered into the ACC contralateral to CCI. The melatonin effect was blocked by the broad MT receptor antagonist luzindole [10 µg but not 5 µg (L10, L5)] injected into the same ACC at 10 min before melatonin (4 µg). *P<0.05, as compared with the sham-vehicle (V) group; ++ P<0.01, as compared with the CCI-vehicle group; ## P<0.01, as compared with the CCI-MT group. B. The same melatonin (MT) treatment also improved the immobility time in the horizontal suspension test (HST) in WKY rat on day 7 after CCI. *P#0.05, as compared with sham and CCI-MT groups.
