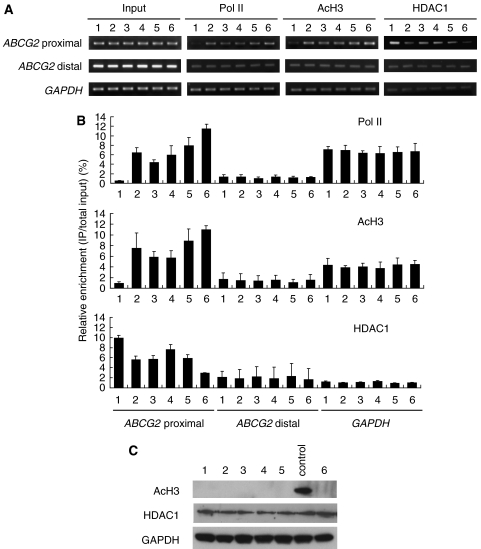
Figure 5.
ABCG2 chromatin in the doxorubicin-selected clones is associated with more RNA Pol II and AcH3 but less HDAC1 than the parental MCF-7 cell line. (A) Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays were performed with parental MCF-7 cells and the doxorubicin-selected clones (Kuo and Allis, 1999). A drug-resistant subline MCF7/FLV1000 (Robey et al, 2001) was employed as a control. Soluble chromatin used in immunoprecipitations had a typical size of <0.5 kb visualisation by gel electrophoresis. RNA Pol II, AcH3 or HDAC1 associated with the distal and proximal region in the ABCG2 promoter were analysed by PCR. Lane 1, parental MCF-7; lane 2, 14 nM clone 2; lane 3, 14 nM clone 6; lane 4, 14 nM clone 13; lane 5, 21 nM clone; and lane 6, MCF7/FLV1000. Input: DNA isolated from the lysate before immunoprecipitation. A representative result from three independent experiments is shown. (B) Quantitative analyses of the occupancy of Pol II, AcH3 or HDAC1 to the ABCG2 promoter (proximal and distal regions) in the cells. The results are expressed as the percentage of immunoprecipitate (IP) over total input DNA. Error bars show the s.d. of three independent experiments. Lanes 1–6 are the same as above. (C) Western blot analysis of AcH3 and HDAC1. Whole-cell lysates were prepared from the parental MCF-7 cells and the various single-step doxorubicin-selected MCF-7 clones for AcH3 (17 kDa) and HDAC1 (65 kDa) detection, respectively. Samples 1–6 are as follows: 1, parental MCF-7; 2, 14 nM clone 2; 3, 14 nM clone 6; 4, 14 nM clone 13; 5, 21 nM clone; and 6, MCF7/FLV1000. As a control, HDAC inhibition by depsipeptide results in hyperacetylation of H3 in the whole-cell lysate (control lane). Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase was used as a loading control for each sample.