Fig. 1. Acute hyperglycemia leads to neuronal injury.
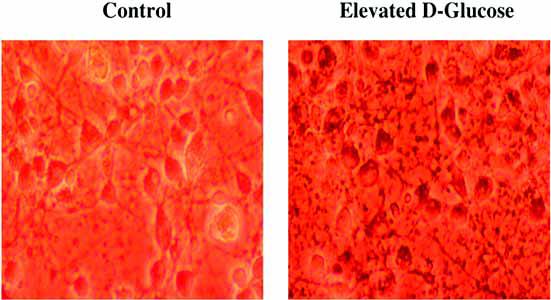
Representative hippocampal neurons obtained from E-19 Sprague-Dawley rat pups were incubated in L-15 growth medium with free serum containing elevated D-glucose of 50 mM for 24 hours at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 and 95% room air. Neuronal cell survival was determined by trypan blue exclusion method and reveals significantly increased dye uptake in injured neurons during hyperglycemia (right panel), but not in untreated control neurons (left panel). Note: Acute neuronal injury with elevated glucose can occur at significantly lower glucose concentrations of 20 mM, but a glucose concentration of 50 mM was chosen for dramatic visualization of cell injury.
