Fig 2. Yki is phosphorylated by Wts in vivo.
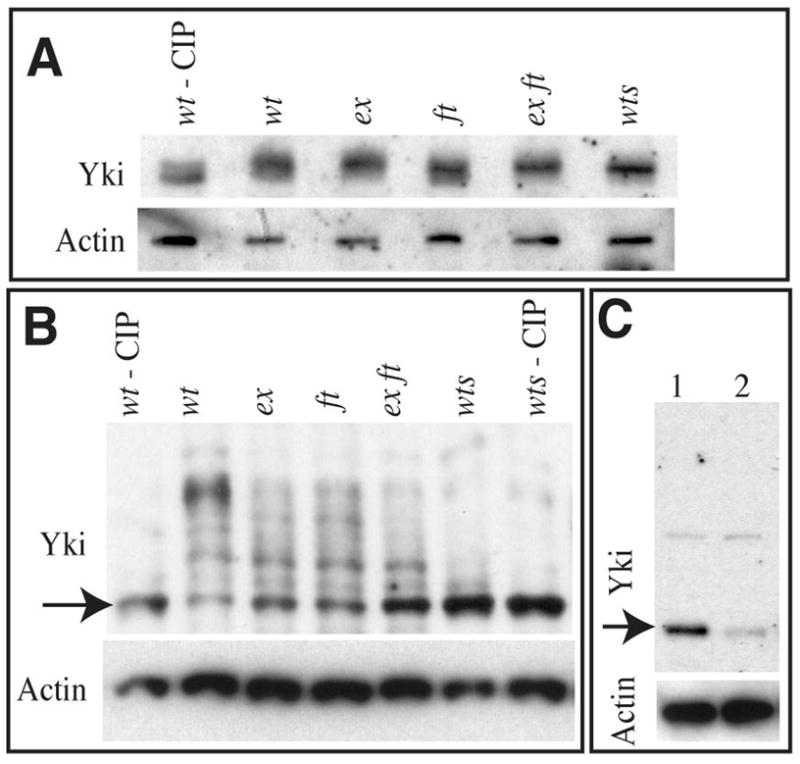
A) Western blots of lysates of wing imaginal discs from animals of wild type, treated with CIP (wt – CIP), wild type (wt), exe1, ftG-rv, exe1 ftG-rv, wtsP2, as indicated, run on a conventional 7.5% PAGE gel, probed with anti-Yki, and, as a loading control, anti-α-Actin. B) Western blot of lysates of wing imaginal discs from animals of wild type, treated with CIP (wt – CIP), wild type (wt), exe1, ftG-rv, exe1 ftG-rv, wtsP2, wtsP2 treated with CIP, as indicated, run on a Phos-Tag gel (25 μM Phos-Tag), probed with anti-Yki, and, as a loading control, anti-Actin. Arrow points to band corresponding to unphosphorylated Yki. C) Conventional 4–15% PAGE gel, probed with anti-Yki (upper panel), and, as a loading control (lower panel) anti-α-Actin. Lane 1 Shows S2 cell lysate treated with ds RNA corresponding to GFP (control), Lane 2 shows lysate from S2 cells treated with ds RNA corresponding to yki. Yki protein (arrow) is reduced, but a faint background band (above) is unaffected.
