Fig 4. Yki phosphorylation and 14-3-3 binding.
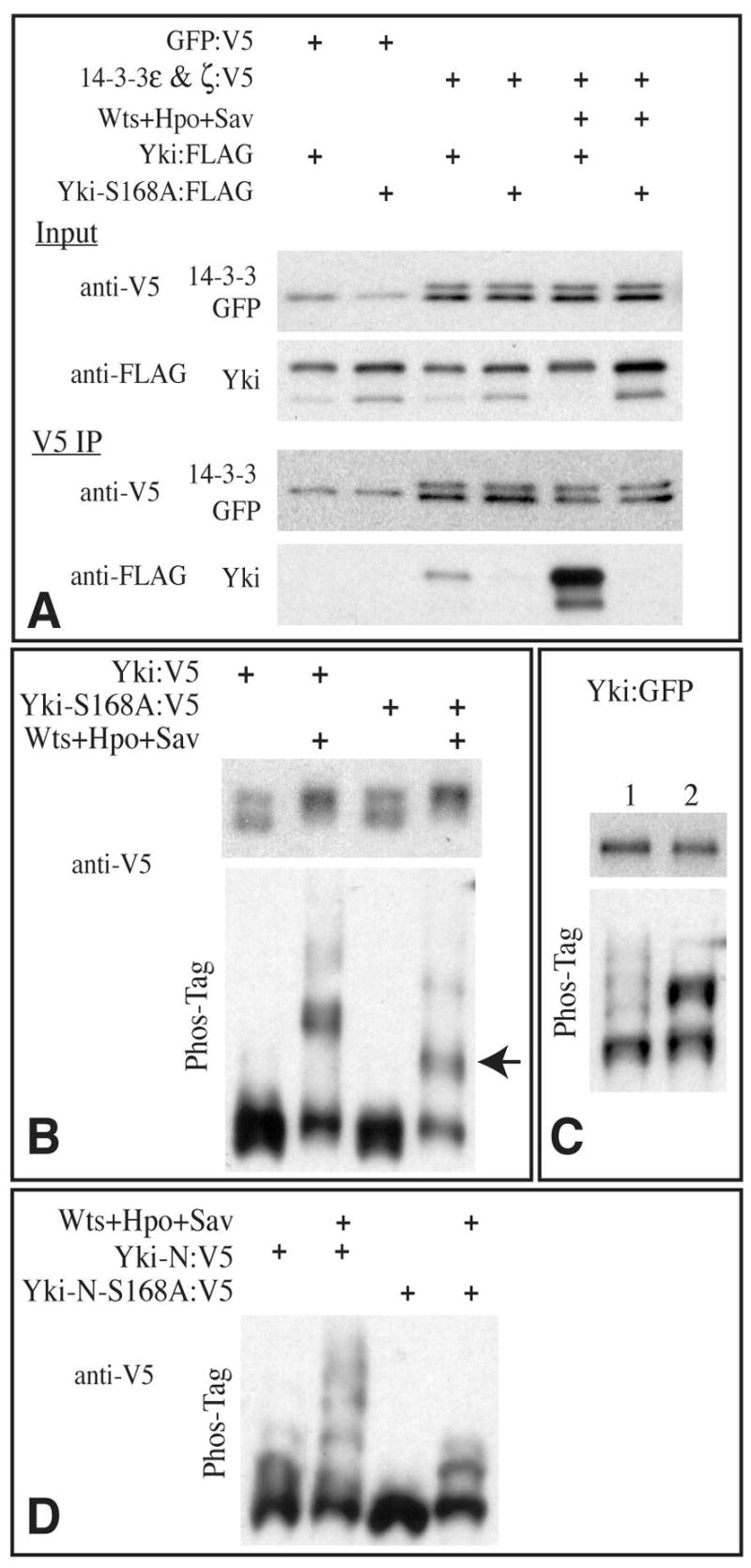
A) Western blots (4–15% PAGE) of samples from S2 cells co-transfected with the indicated proteins. Bottom two panels show blot on material precipitated with anti-V5 beads, upper two panel shows input; GFP:V5 (control protein) and 14-3-3:V5 proteins have similar mobility. B) Western blots (using anti-V5 epitope) on lysates of S2 cells co-transfected to express the indicated proteins. Transfection of Wts, Hpo, and Sav promotes phosphorylation of Yki and Yki-S168A, as revealed both on conventional SDS-PAGE (top panels) and Phos-Tag gels (30 μM Phos-Tag, bottom panels), however a distinct mobility isoform (arrow), representing partially phosphorylated Yki, is observed with Yki-S168A mutant but not wild-type Yki on Phos-tag gels. Transfer of heavily phosphorylated proteins from Phos-Tag gels can be poor, hence they may be underrepresented on these blots. C) Western blots of lysates of wing imaginal discs from animals expressing Yki:GFP (lane 1) or Yki-S168A:GFP (lane 2) under sd-Gal4 control. Upper panel shows conventional SDS-PAGE, lower panel shows a Phos-tag gel (60 μM Phos-Tag) D) Western blot on lysates of S2 cells co-transfected to express the indicated proteins, run on a Phos-tag gel (60 μM Phos-Tag). Yki-N is an N terminal fragment of Yki, comprising the first 240 aa.
