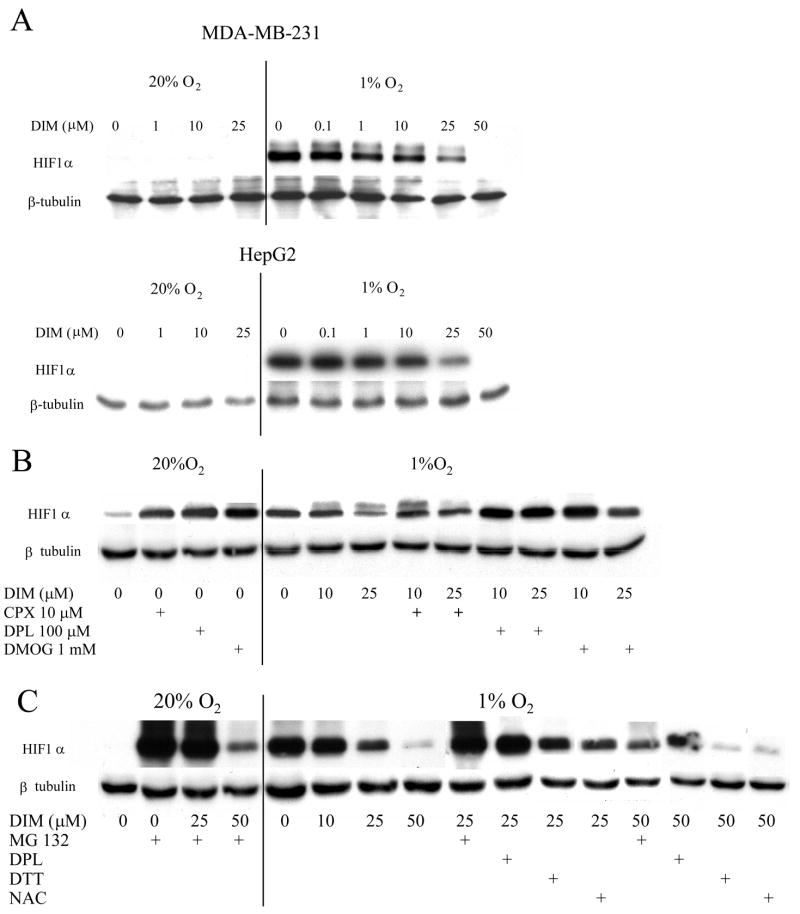
Figure 1. A. DIM inhibits hypoxia-induced increased level of HIF-1α.
MDA-MB-231 and HepG2 cells grown to near confluent density in 6-well plates were treated with various concentrations of DIM in serum free medium and incubated in normoxic or hypoxic conditions for 4 hours. Levels of HIF-1α were measured by Western blot. β-Tubulin was used as a loading control. B. Effects of PHD inhibitors on the level of HIF-1α protein. MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with DIM and the iron chelators ciclopirox olamine (CPX) and 2–2′dipyridyl (DPL) and a metabolic prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor, dimethyloxaloylglycine (DMOG) and incubated in normoxic or hypoxic conditions for 4 hours. Levels of HIF-1αprotein were measured by Western blot. C. Effects of a proteosome inhibitor and of antioxidants on the level of HIF-1a protein. MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with DIM and the proteosome inhibitor, MG132 (20 mM), the PHD inhibitor 2-2′dipyridyl (DPL) (100 mM), and the antioxidants dithiothreitol (DTT) (1 mM) or N-acetyl-cysteine (NAC) (2 mM), and incubated in normoxic or hypoxic conditions for 4 hours. Levels of HIF-1α protein were measured by Western blot. Representative blots are shown. Experiments were reproduced at least three times with identical results.