Abstract
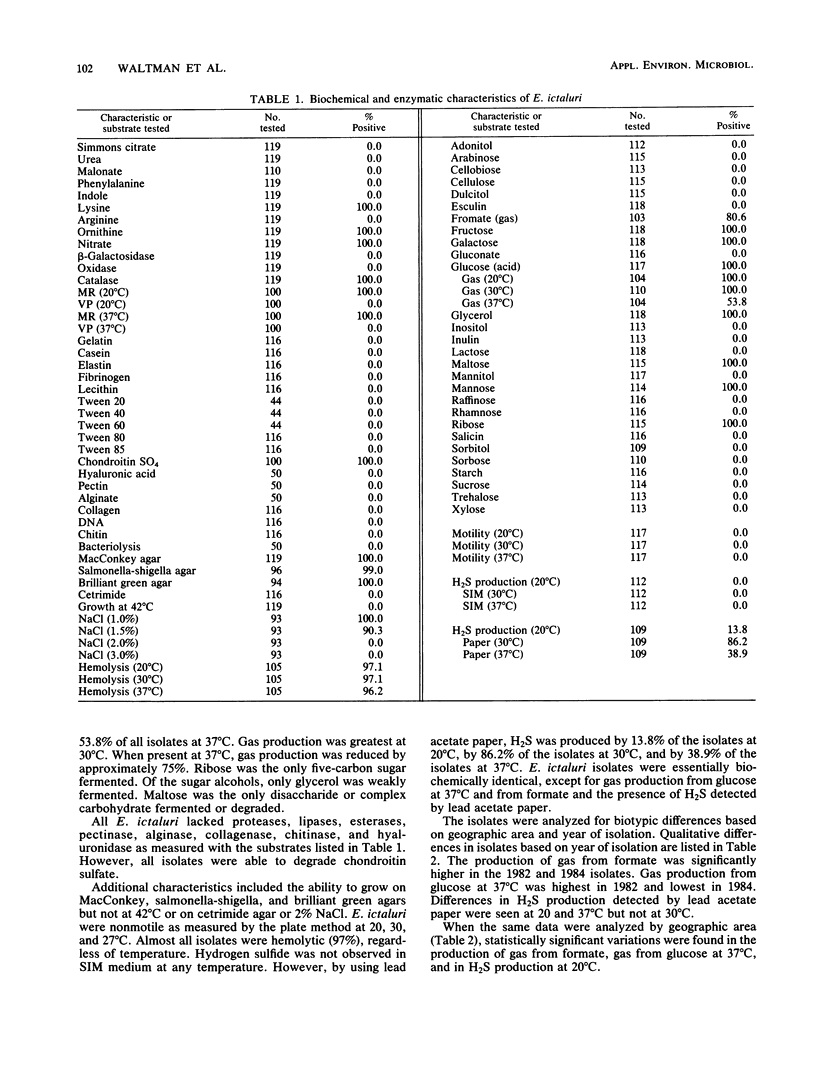
A total of 119 isolates of Edwardsiella ictaluri collected over the last 7 years from several states were biochemically characterized. Although not very reactive biochemically, this bacterium shows a high degree of homogeneity. Differences were found only in the production of gas from formate or from glucose at 37 degrees C and in the production of hydrogen sulfide as detected by lead acetate paper. Analysis of E. ictaluri by year of geographic area indicated that some differences existed, but no clear-cut biotypic variations were found. All isolates studied were capable of degrading chondroitin sulfate, a major component of cartilage, which may be an important virulence factor in the formation of the hole-in-the-head lesion characteristic of infected fish.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Watson J. J., White F. H. Hemolysins of Edwardsiella tarda. Can J Comp Med. 1979 Jan;43(1):78–83. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


