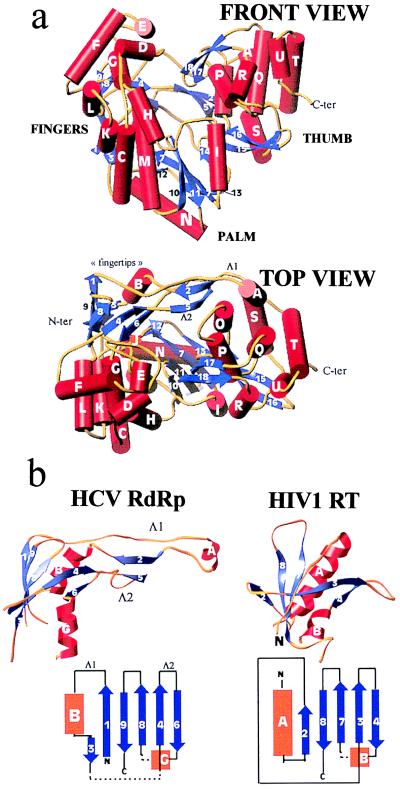
Figure 1.
(a) Front (Upper) and top (Lower) view of the HCV polymerase in a ribbons representation of the polypeptide chain. α-helices (labeled with capital letters) are shown as red cylinders, β-strands (labeled with numbers) as blue arrows, and connecting loops as yellow tubes. The front view has the palm subdomain at the base of the cleft, which is closed at either side by the fingers and thumb and at the back by loops Λ1 and Λ2. (b) The fingertips. Shown is the mixed barrel, composed of β-strands and an α-helix, that lies at the tip of the fingers and aligns structurally between RTs and RdRps. The left panel shows the ribbon diagram of this domain in the HCV polymerase along with a topology diagram. Two long loops (Λ1 and Λ2) emanate from the barrel to close the back of the enzyme. The right panel depicts the corresponding domain of HIV-1 RT in the same orientation. The topology diagram shows that there is a difference in connectivity in the left-most (N-terminal) strands. It is clear that Λ1 is absent but that Λ2 has its counterpart in RT. Broken lines indicate regions in which the polypeptide chain makes excursions into neighboring regions of the fingers to come back and complete the fold of the barrel.