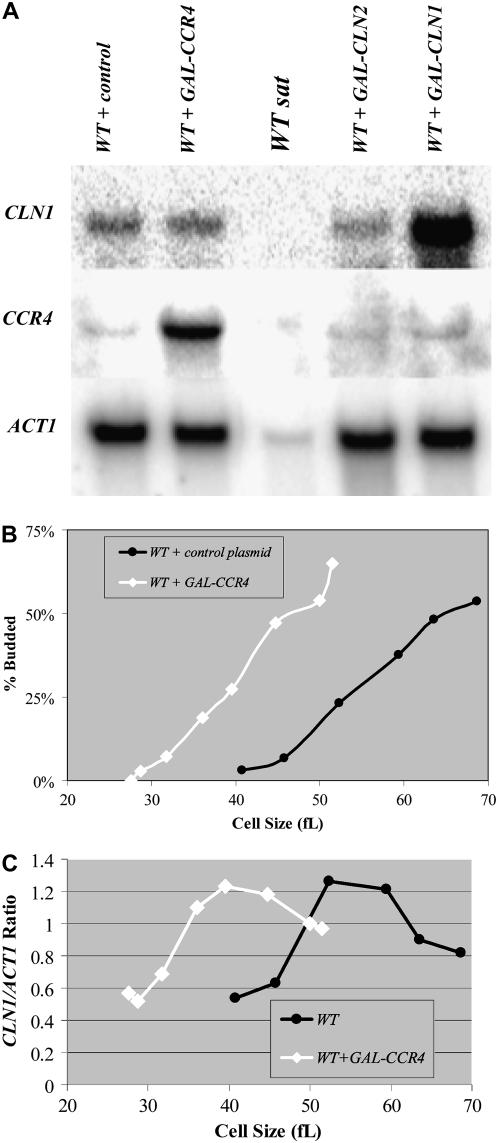
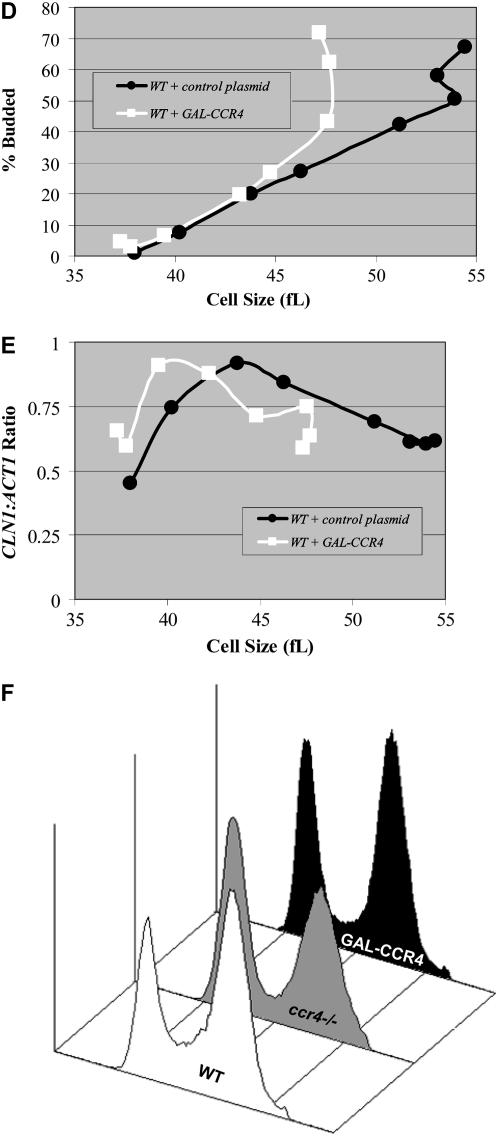
Figure 5.—
Ectopic overexpression of CCR4 modulates the timing of CLN1 and CLN2 expression. Total RNA isolated from the indicated YEPRG grown mid-log-phase cultures was analyzed by Northern analysis. Blots were hybridized with CLN1 and CCR4 probes, and ACT1 probes were used as loading controls (A). RNA from saturated wild-type cultures (WT sat) were used as a negative control because CLN1 is not expressed under these conditions. RNA from cells transformed with GAL-CLN1 constructs (WT + GAL-CLN1) and GAL-CCR4 constructs (WT + GAL-CCR4) were used as positive controls. ACT1 levels are considerably lower in saturated cultures despite even loading. Quantitation revealed that GAL-CCR4 elevated CLN1 and CLN2 (data not shown) levels only very modestly (∼8% higher). Diploid wild-type cells transformed with GAL-CCR4 constructs or control plasmids were grown to mid-log phase in YEPRG, and centrifugal elutriation was used to isolate small, unbudded G1-phase cells. Following elutriation, cells were resuspended in YEPRG fresh medium and regular time points were taken. The percentage of budded cells was plotted as a function of cell size (B). Total RNA was isolated from the elutriation fractions. Blots with RNA from wild-type cells transformed with GAL-CCR4 constructs or control plasmids were hybridized with CLN1 and CCR4 probes. ACT1 probes were used as loading controls. Northerns were quantitated and CLN1/ACT1 ratios were plotted as a function of cell size (C). To determine the effect of induced GAL-CCR4 in similarly sized synchronized cells, cultures were grown in −URA glucose for 12 hr and then transferred to −URA raffinose until mid-log phase. Subsequently, centrifugal elutriation was used to isolate small, unbudded G1-phase cells. Following elutriation, cells were resuspended in YEPRG fresh medium and regular time points were taken. The percentage of budded cells was plotted as a function of cell size (D). Total RNA was isolated from the elutriation fractions. Blots with RNA from wild-type cells transformed with GAL-CCR4 constructs or control plasmids were hybridized with CLN1 and CCR4 probes. CCR4 probes were used to confirm overexpression. ACT1 probes were used as loading controls. CLN1 mRNA expression levels were quantitated and CLN1/ACT1 ratios were plotted as a function of cell size (E). To determine the effect of induced GAL-CCR4, cultures were grown in YEPR and galactose was added to 1% for 3 hr. Flow cytometry analysis revealed that neither induction of GAL-CCR4 nor deletion of CCR4 had strong effects on cell cycle distributions (F). Quantitation revealed that in wild-type cultures 21, 30, and 49% of cells were in G1-, S-, or G2/M-phase. In GAL-CCR4 cultures, 30, 18, and 52% of cells were in G1-, S-, or G2/M-phase while in ccr4Δ cells these numbers were 43, 12, and 45% (F).