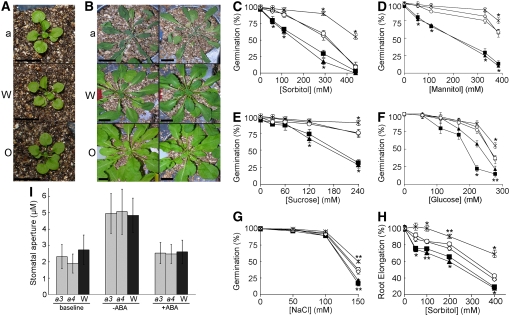
Figure 1.
Altered Water Stress Sensitivities and Stomatal Response of ATHK1 Alleles.
For germination and root elongation experiments, wild-type (open diamonds), athk1-3 (closed squares), athk1-4 (closed triangles), athk1/ATHK1 rescued (open circles), and a 35S:ATHK1 overexpressor (asterisks) from matched seed lots were scored for germination on the indicated concentrations of osmolytes. The percentage of germination or root elongation after 5 d of stress treatment is shown. Each value represents the mean percentage of germination for at least four replicates of at least 100 seeds, or the mean percentage of elongation based on the mean length of a nonstressed control root for at least three replicates of at least 20 roots. Error bars represent the se. Stars above data points represent significance based on a two-tailed t test (* P < 0.01, ** P < 0.05).
(A) Fourteen-day-old seedlings of athk1-3 (a), wild-type (W), and 35S:ATHK1 (O) immediately before the onset of drought stress.
(B) athk1-3 (a), wild-type (W), and 35S:ATHK1 (O) after 6 weeks of drought stress.
(C) Percentage of germination on sorbitol-supplemented media.
(D) Percentage of germination on mannitol-supplemented media.
(E) Percentage of germination on sucrose-supplemented media.
(F) Percentage of germination on glucose-supplemented media.
(G) Percentage of germination on NaCl-supplemented media.
(H) Percentage of root elongation on sorbitol-supplemented media.
(I) Average stomatal aperture of mature adult rosette leaves from wild-type (W; dark gray), athk1-3 (a3; light gray), and athk1-4 (a4; light gray). Leaves were initially held in the dark (baseline). Stomata were then induced to open with light in the presence or absence of ABA. Bars represent the mean of the average stomatal aperture for three experiments (two leaves per experiment, with 20 stomatal aperture measurements per leaf). Error indicated is the sd of the experimental means.