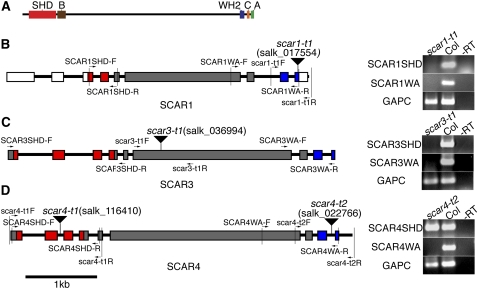
Figure 1.
SCAR Protein Domains and Physical Maps of the Arabidopsis scar T-DNA Insertion Alleles.
(A) Domain organization of a typical plant SCAR family protein, Arabidopsis SCAR4.
(B) to (D) Molecular characterization of SCAR T-DNA insertion alleles. The presence of SHD and WA encoding regions of scar transcripts was assayed using RT-PCR (right panels). Detection of the GAPC gene served as a positive control. Wild-type (Col-0) cDNA and a no-RT reaction served as the positive and negative controls, respectively. The position of the primers used for characterizing T-DNA insertions and the transcription of SHD and WA domains are marked on the physical map by arrows. Red boxes indicate SHD-encoding exons, blue boxes indicate exons encoding the WA domain, gray boxes indicate the regions that encode the nonconserved region in the SCAR proteins, and white boxes indicate the untranslated regions. The inverted triangles label the position of the T-DNA insertions.
(B) Analysis of scar1-t1 (salk_017554) transcripts.
(C) Analysis of scar3-t1 (salk_036994) transcripts.
(D) Analysis of scar4-t2 (salk_022766) transcripts.