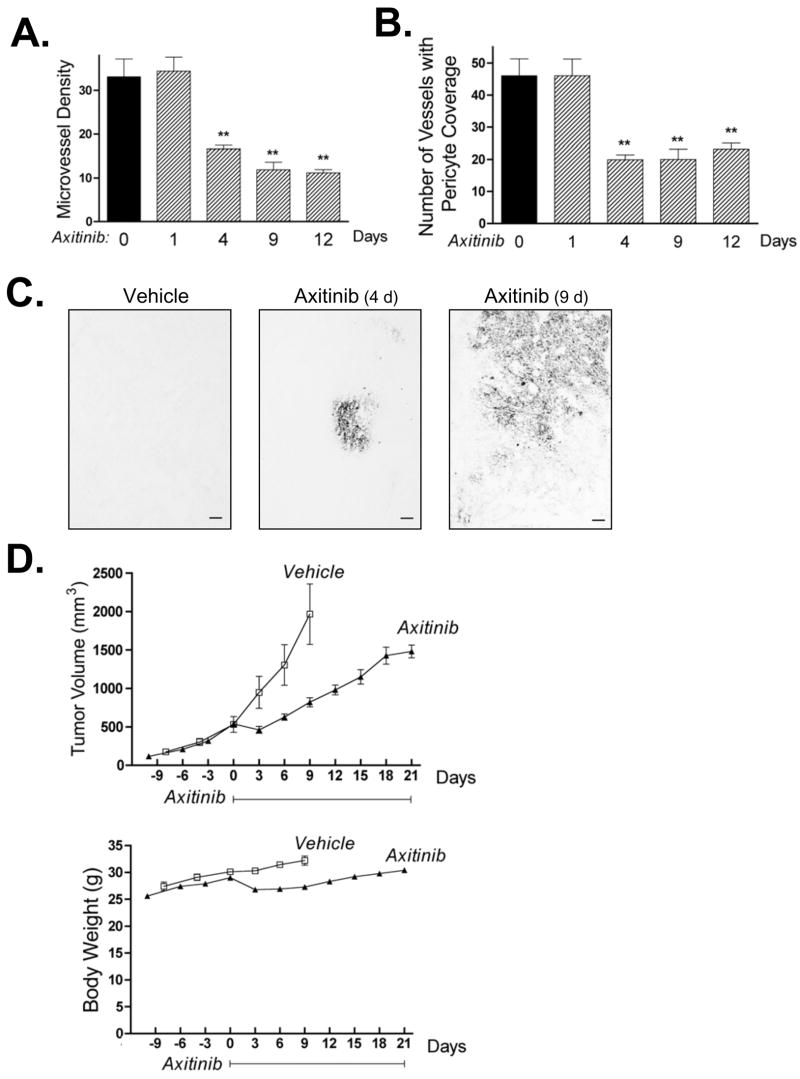
Figure 1. Anti-angiogenic activity and tumor growth delay of axitinib monotherapy in rat 9L gliosarcoma.
9L tumors grown s.c. in scid mice were treated with axitinib for up to 21 days at 25 mg/kg, i.p., sid, as specified in each panel. A. Number of tumor blood vessels per CD31-immunostained 9L tumor section counted at 400x magnification. Axitinib significantly reduced microvessel density after 4–12 days of treatment. B. Impact of axitinib treatment on the number of 9L tumor blood vessels with pericyte coverage, identified as SMA-α-positive blood vessels at 200x magnification. Days of axitinib treatment are indicated along the x-axis, with n = 4 tumors/group and ** p < 0.01 compared to day 0 controls (panels A and B). C. Immunostaining for hypoxia-specific dye pimonidazole revealed an increase in tumor hypoxia after 4 and 9 days of axitinib treatment. Scale bar at bottom right, 100 μm. D. Axitinib treatment initiated on day 0 delayed 9L tumor growth (upper panel, n = 10 tumors/group) with minimal effect on the rate of mouse body weight gain (lower panel). Solid line along x-axis indicates the time period of daily axitinib treatment.