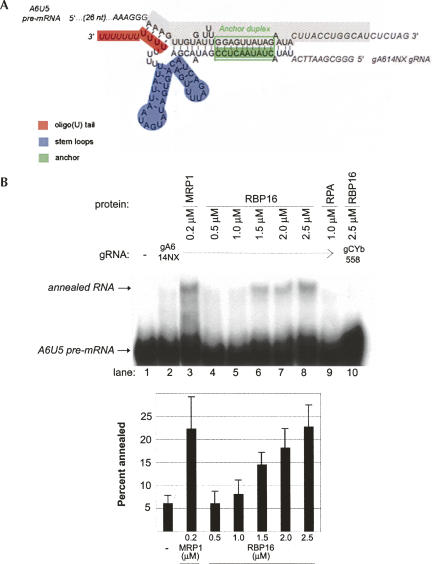
FIGURE 1.
Recombinant RBP16 stimulates annealing of A6 pre-mRNA to cogate gRNA in vitro. (A) Diagram of the annealed A6U5 pre-mRNA (79 nt)/gA6[14]NX substrate pair, depicting gRNA domains and the gRNA/pre-mRNA anchor duplex (green box). The structure is based on the A6 gRNA/pre-mRNA secondary structure prediction from Leung and Koslowsky (1999). (Gray highlighted sequence) The truncated A6U5 41-nt pre-mRNA used in Fig. 3B. (B) Representative annealing assay with radiolabeled A6U5 pre-mRNA and gA6[14]NX gRNA at the indicated protein concentrations. (Lane 1) A6U5 pre-mRNA alone, (lane 2) A6U5 pre-mRNA and gA6[14]NX gRNA in the absence of protein, (lane 3) MRP1 positive control, (lanes 4–8) cognate gRNA/pre-mRNA pair in the presence of increasing RBP16, (lane 9) RPA negative control, (lane 10) reaction with RBP16 and a noncognate gRNA/pre-mRNA pair. Note that the amounts of RBP16 and MRP1 added are consistent with their known RNA binding affinities (Koller et al. 1997; Hayman and Read 1999). The bar graph represents the mean and standard error of the percent of the input pre-mRNA that is annealed to the gRNA from three separate experiments.