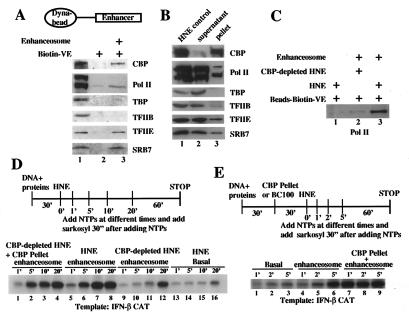
Figure 2.
Recruitment of the CBP-RNA PolII complex by the enhanceosome is the rate-limiting step that determines the speed of PIC assembly at the IFN-β promoter. (A) The IFN-β enhanceosome recruits CBP and the PolII holoenzyme. A biotinylated IFN-β enhancer oligonucleotide (−105 to −40) with or without the enhanceosome was coupled to magnetic Dynabeads and was incubated with 500 μg of HeLa nuclear extract. Western blotting by using CBP, PolII, TBP, TFIIB, TFIIEβ, and SRB7 specific antibodies detected bound proteins. Lane 1 detects the indicated proteins in the HNE, lane 2 corresponds to the precipitated proteins in the absence of the enhanceosome, whereas lane 3 depicts the proteins precipitated by the enhanceosome. (B) Antibodies against CBP coprecipitate components of the RNA PolII holoenzyme. HNE (3.6 mg) was incubated with CBP and p300 specific antibodies (10 μg each), and 1/100 of the pellet or supernatant was analyzed by Western blotting by using antibodies against the depicted. (C) CBP mediates PolII recruitment by the enhanceosome; same as in A except that a CBP-depleted HNE (lane 2) was used in parallel with a complete extract (lane 3). (D) Removal of CBP-RNA PolII holoenzyme from the extract decelerates PIC formation at the IFN-β promoter. Shown is an in vitro transcription experiment performed as detailed in Fig. 1 except that complete (lanes 5–8), CBP-depleted (lanes 9–12), or reconstituted nuclear extracts (lanes 1–4) were used. (E) Same as in D except that the CBP pellet was preincubated with the enhanceosome (lanes 7–9) before the addition of the extract for the indicated amounts of time.