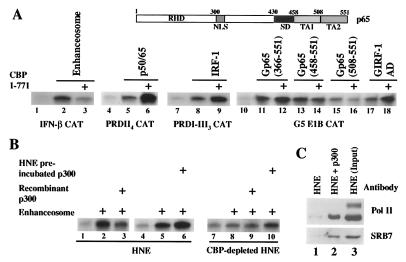
Figure 4.
CBP/p300 that is not complexed with the PolII holoenzyme inhibits enhanceosome-dependent transcription. (A) Shown is an in vitro transcription experiment by using the IFN-β enhancer–promoter as template and the enhanceosome as an activator (lanes 1–3), PRDII4CAT and NF-κB (lanes 4–6), PRDI-III3CAT and IRF-1 (lanes 7–9), or G5E1BCAT and GAL4 p65 or GAL4 IRF-1 fused proteins (lanes 10–18). In lanes 3, 6, 9, 12, 14, 16, and 18, we added 200 ng of GST-CBP (1–771) protein. The top part of the figure depicts a diagrammatic illustration of the p65 protein. The two independent activation domains (TA1 and TA2) as well as the synergism-specific domain required for interaction with CBP are indicated. (B) Shown is an in vitro transcription experiment by using the IFN-β enhanceosome along with 100 ng of baculovirus-expressed and purified, full-length p300. In lanes 1–6, a complete HNE was used whereas in lanes 7–9, a CBP/p300-depleted HNE was used. Recombinant p300 was added either with the enhanceosome lanes 3 and 9 or after preincubation with the complete (lane 6) or CBP/p300-depleted (lane 10) HNE. (C) Recombinant His-tagged p300 (lane 2) was incubated with a HNE followed by the addition of Ni2+-nitrilotriacetic acid agarose beads. The precipitated complexes were washed extensively and immunoblotted by using antibodies against PolII and SRB7. Lane 1 represents nonspecific binding to the agarose beads.