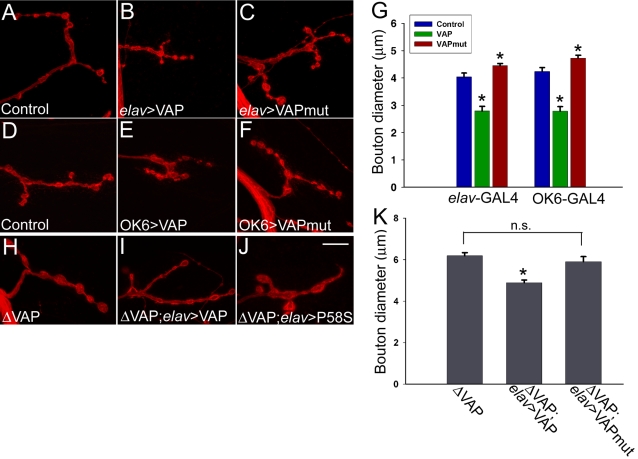
Figure 1. VAPwt and VAPP58S (VAPmut) have differential effects on synaptic morphology at the neuromuscular junction.
Shown are representative synapses on muscle 4 of 3rd instar larvae stained with anti-HRP, which labels the presynaptic membrane. The effect of neuronal overexpression of VAPwt and VAPP58S on bouton morphology was assessed using the pan-neural elav-GAL4 driver (A–C) and the more restricted OK6-GAL4 (D–F). (H–J) Effect of neuronal expression of wild type and mutant VAP on bouton size in VAPΔ166 animals. (A and D) Control synapses on muscle 4 (elav-GAL4/+ and OK6-GAL4/+ respectively). Neuronal overexpression of VAPwt results in smaller boutons (B and E), while expression of VAPP58S leads to an increase in bouton size (C and F). (G). Graphical analysis of bouton size effects. Here and throughout, values shown are mean±SEM. For both drivers, the average size of boutons in animals expressing VAPwt and VAPP58S was found to be significantly different not only with respect to one other but also controls (*, p<0.001, one way ANOVA with Sidak-Holm multiple comparison test). The bouton sizes measured was as follows (µm): elav-GAL4/+ = 4.03±0.14 (n = 16); elav-GAL4/VAPwt = 2.79±0.17 (n = 16); elav-GAL4/ VAPP58S = 4.45±0.08 (n = 24); OK6-GAL4/+ = 4.24±0.14 (n = 20); OK6-GAL4/VAPwt = 2.78±0.17 (n = 11); OK6-GAL4/ VAPP58S = 4.72±0.11 (n = 24). (H–J) A representative synapse on muscle 4 is shown in each panel. (H) In VAPΔ166 mutants, enlarged boutons are observed. (I) Neuronal expression of VAPwt using elav-GAL4 rescues this phenotype by reducing bouton size. (J) Expression of VAPP58S had no effect on bouton size. (K) Histogram comparing bouton size for the genotypes in panels H–K. Mean bouton diameter (µm) for VAPΔ166;UAS-VAPwt/elav-GAL4 (4.89±0.13 (n = 27)) was significantly different from VAPΔ166 (6.18±0.15 (n = 24); p<0.001, one way ANOVA with Sidak-Holm comparison). However, bouton size in VAPΔ166;UAS-VAPP58S/elav-GAL4 (5.9±0.24 (n = 30) did not differ significantly from VAPΔ166 . n.s., not significant. Scale bar, 10 µm.